HP Smart Update Manager Help
Contents
Introduction
HP Smart Update Manager overview
Using this guide
New features of HP SUM 4.2.1
Minimum requirements
Minimum requirements for Windows servers
Minimum requirements for Linux x86 servers
Supported deliverables overview
Obtaining the HP SUM utility
Support and limitations of HP SUM
Deployment from HP SUM
Executing HP SUM
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) for Microsoft Windows
Deploying software using the Integrity Support Pack (ISP) for Microsoft Windows
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack for Linux
Deploying firmware for ProLiant servers using the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD
Deploying firmware using the HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers Bundles
HP SUM User Interface
Deployment scenarios
Graphical deployment on a local host
Scripted deployment on a local host
Deployment to multiple remote hosts
Keyboard support
Local host installations
Selecting the location to check for updates
Download Permission (applicable only for ProLiant servers)
Selecting an installation host
Selecting bundles to filter
Selecting components to install
Component selection pane
Viewing the installation results
Multiple-host installations
Selecting remote hosts or groups
Searching for remote hosts
Managing hosts
Managing groups
Entering credentials for hosts
Selecting bundles to filter on multiple hosts
Selecting components to install on multiple hosts
Firmware update on HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers
Viewing the installation results for multiple hosts
Scripted Deployment
Command-line interface
Command-line syntax
Command-line arguments
Component configuration for Windows components only
Command-line examples
Return codes
Windows smart component return codes
Linux smart component return codes
Linux RPM return codes
Input files
Command-line usage of input files
Input file format and rules
File Encoding
Error Reporting
Input file parameters
Reports
Advanced topics
Software component configuration
Deploying firmware and software simultaneously
Server virtualization detection and support
Configuring IPv6 networks with HP Smart Update Manager
Configuring IPv6 for Windows Server 2003
Configuring IPv6 for Windows Server 2008
Configuring IPv6 for Linux
Troubleshooting
Recovering from a failed ROM upgrade
Recovering from a failed system ROM upgrade
Recovering from a failed option ROM upgrade
Recovering from an installation failure
Collecting trace directories
Recovering from a discovery failure
Troubleshooting connection errors
HP SUM hangs during discovery
Recovering from a loss of Linux remote functionality
Configuring firewall settings
Recovering from a blocked program on Microsoft Windows
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks
Enabling ports in HP Smart Update Manager
Recovering from operating system limitations when using a Japanese character set
Displaying the user-specified reboot message using a Japanese character set
Rebooting with the user-specified reboot message using a Japanese character set
Recovering from Fatal Error - application will exit message
Running in a directory path containing double-byte characters
Recovering from a missing reboot message when running on SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9
Running HP Smart Update Manager on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9
Recovering a lost HP Smart Update Manager connection
HP Smart Update Firmware DVD mounted using iLO virtual media
Component installation fails on a remote target after iLO firmware is installed using HP Smart Update Manager.
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Windows Server 2003 environment
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Windows Server 2008 environment
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Red Hat and Novell SUSE-based Linux environments
HP SUM 'found new hardware' message
Non-matching systems error reported when building source Linux RPMs or installing Linux RPMs built from source
Linux component version discrepancy for source RPMs
HP SUM displays No components found in the selected repository(ies) message
Additional/Optional Actions columns are grayed when HP SUM is maximized
Installation of components failed with 'Update returned an error' when installing Linux RPMs
Issues related to bundle filtering on the Select Items to be Installed and Select Bundle Filter screens
HP SUM fails on Vista due to McAfee firewalls
Virtual Connect firmware upgrade using HP SUM fails if VC reports an invalid or bad health state
Technical support
Reference documentation
Operating system information
HP contact information
Acronyms and abbreviations
Introduction
In this section
HP Smart Update Manager overview
Using this guide
New features of HP SUM 4.2.1
Minimum requirements
Minimum requirements for Windows servers
Minimum requirements for Linux x86 servers
Supported deliverables overview
Obtaining the HP SUM utility
Support and limitations of HP SUM
Deployment from HP SUM
Executing HP SUM
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) for Microsoft Windows
Deploying software using the Integrity Support Pack (ISP) for Microsoft Windows
Deploying software using ProLiant Support Pack for in Linux
Deploying firmware for ProLiant servers using the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD
Deploying firmware using the HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers Bundles
HP Smart Update Manager overview
HP SUM is a technology, included in many HP products for installing and updating firmware and software components on HP ProLiant and HP Integrity servers, enclosures, and options.
HP SUM provides a GUI and a command-line scriptable interface for:
- Deployment of firmware for single or one-to-many HP servers and network-based targets such as iLOs, OAs, and VC Ethernet and Fibre Channel modules.
- Deployment of software for single or one-to-many HP ProLiant servers (supported in Windows and Linux environments) and HP Integrity servers (supported in Windows environments).
|
IMPORTANT: Throughout this document, most references to the deployment of firmware apply only to HP SUM when used with HP ProLiant servers. For HP Integrity servers, deploying firmware using HP SUM only applies to BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers. |
HP SUM has an integrated hardware and software discovery engine that discovers the installed hardware and current versions of firmware and software in use on target servers. This capability prevents extraneous network traffic by sending only the required components to a target host. HP SUM installs updates in the correct order and ensures all dependencies are met before deployment of an update. HP SUM prevents version-based dependencies from destroying an installation, and ensures firmware updates are handled in a manner that reduces any downtime required for the firmware update process.
HP SUM does not require an agent for remote installations because it copies a small, secure SOAP server to the target server for the duration of the installation. After the installation is complete, the SOAP server and all remote files associated with the installation, except installation log files, are removed. HP SUM copies the log files from the remote targets back to the system where HP SUM is executed.
Key features of HP SUM include:
- Dependency checking, which ensures appropriate installation order and dependency checking between components
- Intelligent deployment deploys only required updates
- Simultaneous firmware and software deployment for multiple remote targets in both GUI and CLI modes (ProLiant servers and options only)
- Improved deployment performance
- Local or remote (one-to-many) online deployment
- Local offline firmware deployments with the earlier HP Firmware Maintenance CD or the HP Smart Firmware Update DVD for ProLiant servers and options
- Remote offline deployment when used with the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit or iLO Virtual Media
- GUI- or CLI-scriptable with extensive logging
- Remote command-line deployment
- Support for updating firmware on network-based targets such as the OA, iLO 2/iLO 3 through Network Management Port, and VC Ethernet and Fibre Channel modules on HP ProLiant servers
|
NOTE: HP SUM does not support third-party controllers. This includes flashing hard drives behind these controllers.
|
Using this guide
HP SUM is delivered with many different deliverables. A deliverable is an HP product which contains HP SUM and a set of firmware or software components. Some examples are the ProLiant Support for Windows and the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD. It is important that you review the overview section that follows this section for your deliverable to verify any specific limitations to HP SUM features that apply. Then, you can review the sections describing the features of HP SUM. For more information, see the Supported deliverables overview section.
New features of HP SUM 4.2.1
This release of HP SUM includes the following new support:
- Added the ability to retrieve the Linux RPMs from the HP FTP site (ftp://ftp.hp.com).
- Added the ability to overwrite SNMP configuration parameters for Linux agents.
Minimum requirements
Minimum requirements for Windows operating systems
Minimum requirements for Linux
|
NOTE: For Linux and Windows operating systems, the respective device drivers for the embedded/add-on devices in the target servers must be installed for HP SUM to discover the devices. |
|
NOTE: For a current list of supported operating systems on ProLiant servers, see the PSP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/psp). |
Minimum requirements for Windows servers
To successfully deploy HP SUM on HP ProLiant and Integrity target systems based on a Windows operating system, the following must be available:
- A local administrative system with 512 MB of memory
- Sufficient hard-drive space of at least twice the file size of the components to be deployed
- WMI enabled
- All remote host servers connected to the same network and use TCP/IP to enable the systems to be seen by the administrative system
- An account with administrator privileges on each host server
HP recommends that the user name and password for the administrator account on each host server are the same as those on the local administrative system. If administrator privileges are not set up in this manner, you must have the user name and password for each remote server available. Alternatively, you can use a domain account on the local administrative system that has administrator privileges on the host servers.
- The beginning and ending IP addresses entered for the range of hosts (targets) must be on the same subnet.
- To install firmware on HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers, you must run HP SUM from an x86 or x86 Linux machine. You cannot deploy firmware on a Windows Integrity system from a Windows Integrity system.
|
NOTE: HP Smart Update Manager requires a true Administrator login and not an elevated RUN AS Administrator. If you are unable to perform the net use * \\server\ADMIN$ for Microsoft Windows target servers, you do not have sufficient privileges to run HP Smart Update Manager.
|
|
NOTE: When attempting to use the remote deployment functionality of HP SUM on any edition of Windows Server 2008 or Windows Vista, you must ensure that the File and Print Services feature is enabled and that the File and Print Services exception has been enabled in the Windows firewall. Failure to do so prevents HP SUM from deploying remote Windows target servers.
|
For more information about PSP, see the HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows and Linux User Guide on the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/DocumentIndex.jsp?contentType=SupportManual&lang=en&cc=us&docIndexId=64179&taskId=101&prodTypeId=18964&prodSeriesId=345557).
For more information about ISP implementation by operating system, see the HP Window-on-Integrity website (http://www.hp.com/go/windows-on-integrity-docs), or by server model number, see the HP Integrity Server site (http://www.hp.com/go/integrity_servers-docs).
For more information about HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers, see the HP Integrity and HP 9000 firmware update options on the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/Document.jsp?lang=en&cc=us&objectID=c00399523&jumpid=reg_R1002_USEN).
Minimum requirements for Linux x86 servers
To successfully deploy HP SUM on ProLiant target systems based on a Linux operating system, the following must be available: (HP SUM does not support Linux on HP Integrity systems.)
- A local administrative system with 512 MB of memory
- glibc 2.2.4-26 or later
- gawk 3.1.0-3 or later
- sed 3.02-10 or later
- pciutils-2.1.8-25.i386.rpm or later
To successfully deploy HP SUM on remote target systems based on a Linux operating system, the following must be available:
- tcl-8.x package
- expect-5.x package
Starting with Linux PSP 8.40 and later, ensure the following platform-specific compatibility libraries are also installed.
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4x86 servers:
- compat-libstdc++-296-2.96-132.7.2.i386 or later
- lm_sensors-2.8.7-2.i386 or later
- net-snmp-5.1.2-11.i386 or later
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 AMD64/EM64T servers:
- compat-libstdc++-296-2.96-132.7.2.i386 or later
- lm_sensors-2.8.7-2.x86_64 or later
- net-snmp-5.1.2-11.x86_64 or later
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 x86 servers:
- compat-libstdc++-2.96-2.96-132.7.2.i386 or later
- lm_sensors-2...7-2.i386 or later
- net-snmp-5.3.1-14.e15.i386 or later
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 AMD64/EM64T servers:
- compat-libstdc++-296-2.96-132.7.2.i386 or later
- lm_sensors-2.8.7-2.x86_64 or later
- net-snmp-5.3.1-14.e15.x86_64 or later
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 servers:
|
NOTE: The following versions listed are needed as a minimum. Later versions of these might be used as well. |
|
NOTE: Ensure that each NIC has an IP address assigned. To get the IP address assigned to a NIC, issue the "dhclient" command in the console, which enables the NIC interfaces and retrieves an IP address. If a NIC does not have an IP address, HP SUM appears to hang on start up. |
RHEL6 Console Mode:
|
NOTE: No X console in either x86 or x86_64. User installs base server with defaults and the following RPMs to run HP SUM in silent mode. |
- lm_sensors-libs-3.1.1-10.el6.<arch>.rpm
- net-snmp-libs-5.5-27.el6.<arch>.rpm
- net-snmp-5.5.27.el6.<arch>.rpm
- kernel-headers-2.6.32-71.el6.<arch>.rpm
- redhat-rpm-config-9.0.3-25.el6.noarch.rpm
- kernel-devel-2.6.32-71.el6.<arch>.rpm
- rpm-build-4.8.0-12.el6.<arch>.rpm
- gcc-4.4.4-13.el6.<arch>.rpm
RHEL6 Graphical Mode:
|
NOTE: If the user elects to install the XWindows support, then this applies to both x86 and x86_64. |
|
NOTE: The following items must be the 32-bit version even under x86_64 architecture as HP SUM and several of the RPMs require 32-bit libraries installed. |
- libuuid-2.17.2-6.el6.i686.rpm
- freetype-2.3.11-5.el6.i686.rpm
- libSM-1.1.0-7.1.el6.i686.rpm
- libICE-1.0.6-1.el6.i686.rpm
- libXi-1.3-3.el6.i686.rpm
- libX11-1.3-2.el6.i686.rpm
- libXext-1.1-3.el6.i686.rpm
- libxcb-1.5-1.el6.i686.rpm
- libXau-1.0.5-1.el6.i686.rpm
- libXrender-0.9.5-1.el6.i686.rpm
- libXrandr-1.3.0-4.el6.i686.rpm
- libXfixes-4.0.4-1.el6.i686.rpm
- libXcursor-1.1.10-2.el6.i686.rpm
- fontconfig-2.8.0-3.el6.i686.rpm
- expat-2.0.1-9.1.el6.i686.rpm
- expect-5.44.1.15-2.el6.<arch>.rpm
- zlib-1.2.3-25.el6.i686.rpm
- libstdc++-4.4.4-13.el6.i686.rpm
- net-snmp-5.5-27.el6.<arch>.rpm
In addition, the build directory for RPMs built from source has changed depending on the name of the user building them. Up through RHEL5, the directory had been /usr/src/redhat/RPMS/<architecture>. Under RHEL6, the directory is /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/<architecture> if the user is logged in as root and /$USER/home/rpmbuild/RPMS/<architecture> for users other than root.
For SLES 10 x86 servers:
- compat-2006.1.25-11.2.i586 or later
- compat-libstdc++-5.0.7-22.2.i586 or later
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
For SLES 10 AMD64/EM64T servers:
- compat-2006.1.25-11.2.x86_64 or later
- compat-32bit-2006.1.25-11.2.x86_64 or later
- compat-libstdc++-5.0.7-22.2.x86_64 or later
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
- e2fsprogs-32bit
For SLES 11 x86 servers:
- perl (required to provide the libperl.so)
- libstdc++33-3.3.3-11.9.i586 or later
- perl-SNMP-5.4.2.1-6.3.i586 or later
- net-snmp-5.4.2.1-6.3.i586 or later
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
For SLES 11 AMD64/EM64T servers:
- glib-1.2.10-15.i386 or later
- libstdc++33-32bit-3.3.3-11.9 or later
- perl-SNMP-5.4.2.1-6-3.x86_64 or later
- net-snmp-5.4.2.1-6.3.x86_64 or later
- libnl (required for QLogic and Emulex drivers)
Building NIC source RPMs
You must have the following RPMs, required only on the local Linux system running HP SUM to perform builds of NIC source RPMs:
- gcc-2.96-108.1 or later
- kernel-devel (This RPM is required for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.x. Install the kernel-devel in addition to any kernel-specific devel package such as kernel-xen-devel or kernel-PAE-devel.)
- kernel-syms
- RPM build tools
In addition, components that are compiled from source code (such as NIC drivers) require the presence of the following build tools:
- gcc-2.96-108.1 or later
- cpp-2.96-108.1 or later
- binutils-2.11.90.0.8 or later
- glibc-devel-2.2.4-26 or later
- kernel-headers-<_version_> (The version number depends on which kernel is used.)
|
NOTE: To perform Linux deployments, a root equivalent user account must be used. SSH support must be enabled and firewall opened to enable SSH communications on remote Linux servers or HP SUM is not able to deploy updates. By default, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 and 11 block SSH support through the firewall. If SSH support has been disabled in the firewall, to enable it and open ports, use the yast2 command.
|
|
NOTE: HP SUM is no longer supported on SUSE Enterprise Linux 9.
|
 IMPORTANT: The HP Smart Update Manager does not support cross-platform deployments (for example, deployments from Linux systems to Windows systems). IMPORTANT: The HP Smart Update Manager does not support cross-platform deployments (for example, deployments from Linux systems to Windows systems).
|
Supported deliverables overview
HP SUM support is specific to the deliverable in which it is delivered. Make sure you use the correct version of HP SUM that is released along with the deliverable supporting the environment.
|
NOTE: Not all functionality is available in each version of HP SUM. Before using HP SUM that comes with a deliverable, review the Support and limitations of that version of HP SUM to determine if it has the features that you need.
|
Obtaining the HP SUM utility
The HP SUM utility is available from the following:
- HP ProLiant Support Packs for Windows 7.90 and later
- HP ProLiant Support Packs for Linux 8.40 and later
- HP Smart Update Firmware DVD (for HP ProLiant servers)
- HP Integrity Support Pack for Windows 6.00 and later on Itanium-based systems
- HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers Bundle for Linux
- HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers Bundle for Windows
|
CAUTION: Use the version of HP SUM that comes with the Integrity Support Pack or Integrity Bundle when deploying the components that are included in that deliverable. |
Support and limitations of HP SUM
Before installing HP SUM, use the following table to verify that you are using the appropriate software version.
| HP SUM version |
Delivered with |
Support and limitations |
| 3.7.1 |
HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers Bundles for Windows and Linux |
Support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware - This support is currently available only in HP SUM 3.7.1 and will be integrated into a future release of HP SUM
No support for downloading the latest versions of components from the HP FTP site
No report functionality is available
|
| 4.0.0 |
For ProLiant Servers:
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows 8.40
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Linux 8.40
HP Smart Update DVD 9.0
For ProLiant Workstation Blades:
HP Workstation Support Pack for Windows for HP WS460c G6 Blade
HP Smart Update DVD 9.0 (offline only)
|
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware or Integrity Support Pack
|
| 4.0.0.64 |
HP Integrity Support Pack for Windows on Itanium-based systems
|
Support for Integrity Support Pack for Windows 7.00
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware deployment
No support to download the latest components available from ftp.hp.com through HP SUM GUI and command line options
|
| 4.0.1 |
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows 8.50
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Linux 8.50
|
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware or HP Integrity Support Pack
|
| 4.0.2 |
HP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.10
|
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware or HP Integrity Support Pack
|
| 4.1.0 |
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows 8.60
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Linux 8.60
HP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.20
|
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware or HP Integrity Support Pack
|
| 4.1.1 |
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Linux 8.62
|
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware or HP Integrity Support Pack
|
| 4.2.1 |
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Linux 8.70
HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows 8.70
HP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.30
|
No support for BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers firmware or HP Integrity Support Pack
|
Deployment from HP SUM
In this Section:
Executing HP SUM
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) for Microsoft Windows
Deploying software using the Integrity Support Pack (ISP) for Microsoft Windows
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack for Linux
Deploying firmware for ProLiant servers using the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD
Deploying firmware for HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers
Executing HP SUM
HP SUM provides three modes of execution for users:
- GUI - For firmware and software deployments
- Express - For software deployments only (local host only)
- Scripted - For firmware and software deployments running silently
HP SUM enables you to deploy to both local and remote deployments. HP SUM can run in both standard Windows and Linux operating systems in online mode and in offline mode (available on HP Smart Update Firmware DVD) through special boot environments based on Linux boot kernels as long as the prerequisites are met.
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack (PSP) for Microsoft Windows
The HP SUM utility delivered with the Windows PSP enables you to deploy software components from a single, easy-to-use interface for ProLiant server and options.
This utility enables legacy support of existing software and firmware components while simplifying the overall deployment process. You do not have to run the SETUP executable files SETUPC.EXE, SETUPEX.EXE, and SETUP.EXE, because the HP SUM utility now provides this functionality. The utility also provides installation logic and version control that automatically verifies dependencies, installing only the correct updates for optimal configuration.
Users can now deploy the components simultaneously for ProLiant servers and options. For more information about simultaneous deployment, see Deploying firmware and software simultaneously.
For more information about PSP, see the HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows and Linux User Guide on the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/DocumentIndex.jsp?contentType=SupportManual&lang=en&cc=us&docIndexId=64179&taskId=101&prodTypeId=18964&prodSeriesId=345557).
HP SUM delivered with HP Workstation Support Pack supports the software deployment on Windows for HP ProLiant WS460c G6 Blade. This support is available for the local host only.
Deploying software using the Integrity Support Pack (ISP) for Microsoft Windows
The HP SUM utility enables you to deploy Windows ISP software components for HP Integrity Servers from a single, easy-to-use interface. This utility enables legacy support of existing software components while simplifying the overall deployment process. You do not have to run the SETUP executable files SETUPC.EXE, SETUPEX.EXE, and SETUP.EXE, because the HP SUM utility now provides this functionality. The utility also provides installation logic and version control that automatically check for dependencies, installing only the correct updates for optimal configuration.
|
NOTE: In HP Integrity servers, HP SUM does not support the ability to download the latest components from ftp.hp.com, as these components are not in the catalog on the HP FTP site. |
|
NOTE: Use the version of HP SUM that comes with the ISP when deploying the components that are included in that deliverable. |
For more information about ISP implementation by operating system, see the HP Window-on-Integrity website (http://www.hp.com/go/windows-on-integrity-docs), or by server model number, see the HP Integrity Server site (http://www.hp.com/go/integrity_servers-docs).
Deploying software using the ProLiant Support Pack for Linux
Beginning with PSP for Linux 8.40 or later, the HP SUM utility enables you to deploy Linux PSP software components (RPMs) from a single, easy-to-use interface. The same manageability is present with added flexibility and more features for added convenience and enhanced functionality. HP SUM provides new GUI and a command-line, scriptable interface for deployment to target servers. HP SUM discovers and displays all components that are available for installation on the local system and enables the flexibility to choose which components to install or not install. Additionally, the HP SUM utility enables software deployment for multiple HP ProLiant servers from a single GUI.
For more information about PSP, see the HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows and Linux User Guide on the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/DocumentIndex.jsp?contentType=SupportManual&lang=en&cc=us&docIndexId=64179&taskId=101&prodTypeId=18964&prodSeriesId=345557).
Deploying firmware for ProLiant servers using the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD
The HP Smart Update Firmware DVD provides a collection of firmware bundles containing HP SUM and firmware for ProLiant servers in an ISO image that can be used either in offline (either an automatic or interactive mode), or online (either a scripted or interactive mode). The HP Smart Update Firmware DVD provides firmware for supported HP ProLiant servers and options. The Firmware DVD contains all the firmware for the supported HP ProLiant servers including BladeSystem enclosures and Virtual Connect firmware.
- In offline mode, the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD boots a small Linux kernel and enables firmware updates to occur on a single server using the HP SUM software.
- In online mode, users can leverage the autorun utility to launch HP SUM or browse the DVD to the \hp\swpackages directory and execute it directly.
All firmware smart components are placed in the \hp\swpackages directory for use by HP SUM. If additional firmware smart components are required, then the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD can be copied to a USB key, and these additional components added to the \hp\swpackages directory. If HP SUM supports the type of firmware added, then it is automatically added the next time HP SUM is executed.
 CAUTION: The HP Smart Update Firmware DVD and its contents must be used only by individuals who are experienced and knowledgeable with HP SUM. Before using HP SUM to update firmware, back up the target server, and take all other necessary precautions so that mission-critical systems are not disrupted if a failure occurs. CAUTION: The HP Smart Update Firmware DVD and its contents must be used only by individuals who are experienced and knowledgeable with HP SUM. Before using HP SUM to update firmware, back up the target server, and take all other necessary precautions so that mission-critical systems are not disrupted if a failure occurs.
|
|
NOTE: Because firmware might be able to update only in online or offline mode for some components, you might need to execute the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD both online and offline to update all the firmware in an enclosure. |
HP SUM stores host and group information from session to session. However, user names, passwords, and existing credentials are not stored in a session or from session to session.
Use OA version 2.51 or later to get a list of all major firmware versions deployed in your enclosure, using the Rack Firmware link on the main OA web page. HP supports the current and two previous versions of the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD.
|
NOTE: The Onboard Administrator and Virtual Connect Ethernet and Fibre Channel Modules are supported only in online deployments on HP ProLiant servers.
|
|
NOTE: You can add firmware components to the USB drive key in the /hp/swpackages directory.
|
 IMPORTANT: Before deploying firmware updates to a target server, be sure that a recent backup of the target server is available in the event the deployment procedure fails. IMPORTANT: Before deploying firmware updates to a target server, be sure that a recent backup of the target server is available in the event the deployment procedure fails.
|
For more information about deploying firmware on HP ProLiant servers, see the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD User Guide on the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/DocumentIndex.jsp?contentType=SupportManual&lang=en&cc=us&docIndexId=64179&taskId=101&prodTypeId=18964&prodSeriesId=345557).
|
NOTE: Currently, HP SUM cannot be used to deploy firmware on HP Integrity servers except for HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers. |
HP SUM supported firmware for HP ProLiant servers
| Component | Supported |
| HP ProLiant ML/DL/SL series System ROM | Yes |
| HP Workstation WS460c G6 Blade ROM | Yes, offline only |
| HP ProLiant Blade Servers ROM | Yes |
| HP ProLiant 100-series Servers ROM | Yes |
| iLO 2 firmware | Yes, local and remote |
| iLO 3 firmware*** | Yes, local and remote |
| LO-100 firmware*** | Yes |
| Broadcom NIC firmware | Yes |
| Intel NIC firmware | No |
| QLogic NIC firmware | Yes, offline only |
| Mellanox NIC firmware | Yes |
| Power Management Controller firmware | Yes |
| Smart Array Controller firmware | Yes |
| SAS and SATA hard drive firmware behind Smart Array controllers | Yes |
| SAS and SATA hard drive firmware behind non-Smart Array controllers | No |
| Emulex, QLogic, and Brocade Fibre Channel Host Bus Adapter firmware | Yes, offline only |
| Tape blade firmware | Yes |
| Virtual Connect firmware* | Yes, online only |
| HP StorageWorks 600 Modular Disk System (MDS600)** | Yes, offline only |
| HP 3Gb SAS BL Switch firmware | Yes, online only |
| Onboard Administrator Firmware**** | Yes, online only |
| CPLD/SPLD***** | Yes |
When updating HP ProLiant blade servers in an HP BladeSystem Matrix, do not select ftp.hp.com to download the latest components. Ensure the component source contains versions of components that match the BladeSystem Matrix Compatibility chart before using HP SUM to deploy any software of firmware.
To view the BladeSystem Matrix compatibility chart, see the HP website (www.hp.com/go/matrixcompatibility.)
*Virtual Connect firmware components can be downloaded and added to the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD by creating a USB key using the USB Key Utility. The latest version of the Virtual Connect firmware components can be obtained from the HP BladeSystem Firmware Maintenance website (http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystemupdates).
HP SUM 4.1.0 and later support deploying Virtual Connect firmware version 3.x and later only. HP recommends using VCSU to deploy VC firmware version 2.3x and earlier.
HP SUM does not upgrade the VC firmware in any situation where the Virtual Connect health state is reported as bad or invalid.
**MDS600 firmware update requires HP SUM 3.6.0 or later. All blades in an enclosure with Smart Array P700M controllers, except the blade doing the update, must be turned off before the firmware update process is initiated. MDS600 firmware can only be updated using the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD in offline mode.
***Direct deployment of LO-100 (using the LO-100 BMC IP) or iLO 3 firmware from the remote hosts section is not supported. To flash the LO-100 or iLO 3 firmware component, you must go through the server IP.
****Downgrading the Onboard Administrator firmware from a new major release to an older release version (for example, 3.x to 2.x) is not supported in HP SUM. Downgrading to a minor version from within a major version is supported (for example, 2.60 to 2.52). To manually install a previous version of the Onboard Administrator firmware, select the Force downgrade box from the Firmware Information section on the Onboard Administrator GUI screen. Select the firmware file by browsing locally or by locating a URL using the input boxes. For any limitations in using older Onboard Administrator firmware or other downgrade options, see the HP Onboard Administrator User Guide.
*****HP SUM 4.1.0 and later has the ability to flash the CPLD/SPLD for HP ProLiant BL280 G6 and BL490 G6 servers. The CPLD/SPLD flash components are not part of the HP SUM deliverable and must be manually downloaded from the HP FTP site (ftp://ftp.hp.com). Run HP SUM and deploy the CPLD/SPLD component.
IMPORTANT: After flashing the CPLD/SPLD, you must cycle power for the changes to take effect. Remove the blade from the enclosure, and then wait 30 seconds before re-inserting it. Pressing the power button is not sufficient.
When performing this flash upgrade from a Linux OS environment, the HP ProLiant Channel Interface Device Driver for iLO2 must be installed and running before executing the upgrade. If the HP ProLiant Channel Interface Device Driver is not installed and running, the following error message displays: "The software is not supported for installation on this system. You must install the iLO Channel Interface driver to use this component."
No driver requirement exists for the Windows OS flash upgrade. |
HP USB key utility
The HP USB Key Utility enables you to copy the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD contents to a USB memory key. You can then run the Firmware update applications from a USB key instead of the DVD. Insert a USB key containing the Firmware DVD ISO image created by using the HP USB Key Creator for Windows utility into a server USB port or the SUV (Serial-USB-Video) cable attached to the blade.
For Windows operating systems, the HP USB Key Creator for Windows utility must be downloaded from the HP website (http://www.hp.com) and installed on a workstation. After installation, the utility places a shortcut in the HP System Tools folder in the Programs start menu.
To create your bootable drive key and copy the contents of the DVD:
- Insert the HP USB drive key in an available USB port.
- Select the HP USB Key Utility shortcut in the HP System Tools folder.
- Complete each step presented by the application.
- The HP USB Key Creator formats the USB key. Ensure that you are using a USB key that is at least 1GB in size and does not contain any valuable files.
For Linux, the USB key can be created manually:
- Obtain SYSLINUX 3.75 or higher from http://www.syslinux.zytor.com, and download it to a Linux workstation.
- Install the SYSLINUX RPM obtained in step 1.
- If a directory does not already exist, create one for the USB key mount point, for example, mkdir /usbkey.
- Insert the USB key, and then mount it. The device mount point might vary, depending on whether other SCSI drives are also installed on the server. Therefore, the device mount point can be sdb1, sdc1, and so on.
mount /dev/sda1 /usbkey
- Use the ./syslinux /usbkey command to write out the boot partition to the USB key. Failure to run this command might lead to a key that does not boot the Firmware DVD until the SYSLINUX command is successful.
- Create a directory to mount the DVD image, for example, mkdir /cd_mount_point.
- Insert the Firmware DVD or mount the Firmware DVD ISO through a loopback:
mount /dev/cdrom /cd_mount_point or mount -t iso9660 firmware-<version>.iso /cd_mount_point -o loop
- Change to the /usb directory on the DVD:
cd /cd_mount_point/usb
- Execute the usbcreator.sh shell script passing in the DVD mount point and the USB mount point to move the Firmware DVD files to the USB key:
./usbcreator.sh /cd_mount_point /usbkey
- If additional components must be added to the USB, copy the components into the /hp/swpackages (Linux) or the \hp\swpackages (Windows operating system) directory. If the version can support the type of components added, then HP SUM picks them up automatically.
- Unmount the DVD and the USB key. This must match the initial mount point in step 4.
umount /dev/cdrom
umount /dev/sda1
- Remove the USB key and DVD.
Using a hard drive
- Copy the contents of the \hp\swpackages directory from the DVD or ISO image to a directory on the hard drive where HP SUM is to be executed.
|
NOTE: Ensure that execute privileges are available in Linux by using the chmod 700 * command. By default, the files are copied off the DVD in Linux as read-only with no execution privileges. |
- Copy any updated files into the same directory where the files were copied in step 1.
- Execute HP SUM to have the new components recognized.
Deploying components not on HP Smart Update Firmware DVD
Make sure you use the correct version that is released along with the deliverable supporting the environment.
If you have components that are not on the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD that you want to deploy to a ProLiant server or option, you can include other smart components in the HP SUM environment. To deploy software and firmware components that are not on the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD:
- Obtain the components from the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
- Create a bootable USB key, or copy the \hp\swpackages directory to the hard drive, and then remove the read-only bit (Linux only).
- Add the components to the \hp\swpackages directory on the USB key or to the directory on the hard drive with the components from the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD.
- Start HP SUM.
- On the Source Selection screen, you can specify the directory where all of the components are located as well as select the Check ftp.hp.com (for ProLiant servers) checkbox if you want to include the latest version of software and firmware components from the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
- Select the checkbox for non-bundle versions, and then click OK.
Trusted Platform Module
The TPM, when used with BitLocker, measures a system state and, upon detection of a changed ROM image, restricts access to the Windows file system if the user cannot provide the recovery key. HP Smart Update Manager detects if a TPM is enabled in your system. If a TPM is detected in your system or with any remote server selected as a target, for some newer models of ProLiant, HP Smart Update Manager utilities for iLO, Smart Array, NIC, and BIOS warn users prior to a flash. If the user does not temporarily disable BitLocker and does not cancel the flash, the BitLocker recovery key is needed to access the user data upon reboot.
A recovery event is triggered if:
- The user does not temporarily disable BitLocker before flashing the System BIOS when using the Microsoft BitLocker Drive Encryption.
- The user has optionally selected to measure iLO, Smart Array, and NIC firmware.
If HP Smart Update Manager detects a TPM, a pop-up warning message appears.
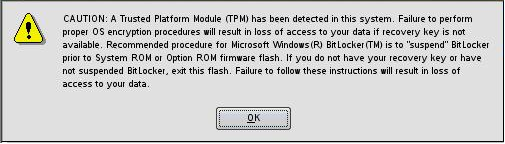
To enable firmware updates without the need to type in the TPM password on each server, the BitLocker Drive Encryption must be temporarily disabled. Disabling the BitLocker Drive Encryption keeps the hard drive data encrypted. However, BitLocker uses a plain text decryption key that is stored on the hard drive to read the information. After the firmware updates have been completed, the BitLocker Drive Encryption can be re-enabled. Once the BitLocker Drive Encryption has been re-enabled, the plain text key is removed and BitLocker secures the drive again.
|
NOTE: Temporarily disabling BitLocker Drive Encryption can compromise drive security and should only be attempted in a secure environment. If you are unable to provide a secure environment, HP recommends providing the boot password and leaving BitLocker Drive Encryption enabled throughout the firmware update process. This requires the /tpmbypass parameter for HP Smart Update Manager or the firmware update is blocked.
|
To temporarily disable BitLocker support to allow firmware updates, perform the following:
- Click Start, and then search for gpedit.msc in the Search Text box.
- When the Local Group Policy Editor starts, click Local Computer Policy.
- Click Computer Configuration>Administrative Templates>Windows Components>BitLocker Drive Encryption.
- When the BitLocker settings are displayed, double-click Control Panel Setup: Enable Advanced startup options.
- When the dialog box appears, click Disable.
- Close all the windows, and then start the firmware update.
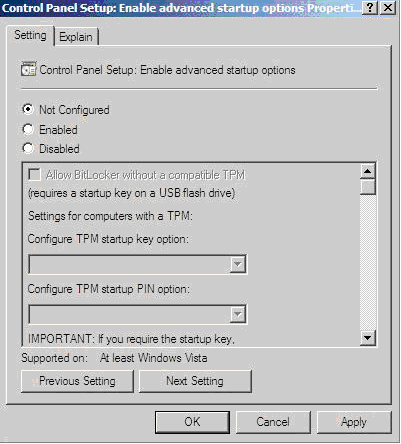
To enable advanced startup options, use the following command:
cscript manage-bde.wsf -protectors -disable c:
When the firmware update process is completed, the BitLocker Drive Encryption support can be re-enabled by following steps 1 through 4 but clicking Enabled in step 5 instead. The following command can be used to re-enable BitLocker Drive Encryption after firmware deployment has completed.
cscript manage-bde.wsf -protectors -enable c:
TPM scenarios
The following table discusses the TPM detection scenarios that you might encounter.
| Scenario |
Result |
| If the TPM is detected and enabled, the installation is not silent, and a system ROM must be updated. | A pop-up warning message appears. After OK is selected, you can continue. The installation is not canceled. |
| If the TPM is detected and enabled, the installation is silent, the /tpmbypass switch is not given, and any firmware updated must be applied to the server. |
No pop-up warning appears. A new log file is generated (%systemdrive%\cpqsystem\log\cpqstub.log). Because the installation is silent, the installation is terminated and cannot continue. |
| If the TPM is detected and enabled with Option ROM Measuring, the installation is not silent, and a system ROM must be updated. | A pop-up warning message appears. After OK is selected, you can continue. The installation is not canceled. |
| If the TPM is detected and enabled with Option ROM Measuring, the installation is silent; the /tpmbypass switch is not given, and any firmware updated must be applied to the server. |
No pop-up warning appears. A new log file is generated (%systemdrive%\cpqsystem\log\cpqstub.log). Because the installation is silent, the installation is terminated and cannot continue. |
| If the TPM is detected and enabled, the installation is silent, and the /tpmbypass switch is supplied. |
The installation occurs. |
Other scenarios do not affect the normal installation procedure.
Deploying firmware using the HP Smart Update Firmware - HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers Bundles
You can only deploy this firmware in HP SUM, included in their respective Windows and Linux bundles. For supported HP SUM versions, see Support and limitations.
Deploying firmware to the HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers is done remotely and is the same as deploying other firmware like OA or VC with the following exceptions:
- You must specify the IP address of the iLO-3 MP on the server as the target to be updated.
- On the Select Items to be Installed screen, you must choose whether you want to Upload and Activate or Upload but Do Not Activate. If you choose not to activate immediately, the firmware is only updated when the server is rebooted.
|
NOTE: In HP Integrity servers, HP SUM does not support the ability to download the latest components from ftp.hp.com, as these components are not in the catalog on the HP FTP site. |
|
NOTE: Use the version of HP SUM that comes with the Integrity Bundle when deploying the firmware to the HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers. |
HP SUM supported firmware for HP Integrity servers
| Component |
Supported |
| Online System ROM |
Yes |
| FPGA firmware |
Yes |
| iLO-3 MP firmware |
Yes |
| Power Monitor firmware |
Yes |
HP SUM User Interface
In this Section:
Deployment scenarios
Graphical deployment on a local host
Scripted deployment on a local host
Deployment to multiple remote hosts
Keyboard support
Local host installations
Selecting the location to check for updates
Download Permission (applicable only for ProLiant servers)
Selecting an installation host
Selecting bundles to filter
Selecting components to install
Component selection pane
Viewing the installation results
Multiple-host installations
Selecting remote hosts or groups
Searching for remote hosts
Managing hosts
Managing groups
Entering credentials for hosts
Selecting bundles to filter on multiple hosts
Selecting components to install on multiple hosts
Firmware update on HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers
Viewing the installation results on multiple hosts
Deployment scenarios
HP SUM deploys firmware and software on a local host or one or more remote hosts. The remote hosts must be online and running the same operating system as the system running HP SUM. For example, when the remote hosts are running Linux, HP SUM must also be running on a Linux operating system.
The following table describes when typical HP SUM deployment scenarios are used.
| Scenario |
Used when |
| Graphical deployment on a local host |
- Are not familiar with command line tools.
- Are deploying components on a local, single host.
- Do not require scripting.
|
| Scripted deployment on a local host |
- Are familiar with command line tools.
- Are deploying components on a local, single host.
- Must perform a customized, scripted deployment.
|
| Graphical deployment to a remote host |
- Are not familiar with command line tools.
- Are deploying components on one or more remote hosts.
- Do not require scripting.
|
| Scripted deployment to a remote host |
- Are familiar with command line tools.
- Are deploying components on one or more hosts.
- Must perform a customized, scripted deployment to one or more host systems.
|
Graphical deployment on a local host
To deploy components to a single local host, use the HP SUM GUI.
- Ensure all minimum requirements are met as described in "Minimum requirements."
- Ensure that the components to be deployed are accessible to the local host.
For information about performing the deployment using the GUI, see "Local host installations".
Scripted deployment on a local host
To deploy components to a local host using the command-line interface:
- Ensure all minimum requirements are fulfilled as described in "Minimum requirements."
- Ensure that the components to be deployed are accessible to the local host.
- Create a script to customize the deployment. See "Scripted deployment" for more information.
- Execute the script.
Deployment to multiple remote hosts
|
NOTE: A remote host can be the IP address or DNS name of a remote server, remote iLO NIC port, Virtual Connect Ethernet or Fibre Channel Module for c-Class BladeSystem, BladeSystem Onboard Administrator, or 3 Gb SAS BL Switch firmware. |
To deploy components to multiple remote hosts using the GUI:
- Ensure that all minimum requirements are met as described in "Minimum requirements."
- Ensure that the components to be deployed are accessible to the administrative system.
For more information about performing the deployment using the graphical interface, see "Multiple-host installations using the GUI".
To deploy components to multiple remote hosts using the CLI:
- Ensure that all minimum requirements are met as described in "Minimum requirements."
- Ensure that the components to be deployed are accessible to the administrative system.
- Create a script to customize the deployment. For more information, see "Scripted deployment."
- Execute the script.
Keyboard support
The HP Smart Update Manager graphical user interface has accelerator keys that enable you to manage and control common tasks quickly. To ensure proper navigation, the following are a few reminders.
- Depending on the operating system, you must press ALT to see the task corresponding to the underlined letter.
- The accelerator keys work by pressing ALT + the underlined letter.
- Press Space to select items such as hosts or groups.
- Press Tab to select from a list, and then press the arrow keys to toggle radio buttons.
Local host installations
HP Smart Update Manager can deploy smart components on a local host or on one or more remote hosts. You can deploy components on a local host by using the HP Smart Update Manager GUI. To access the HP Smart Update Manager, see Deployment Options.
Selecting the location to check for updates
The Source Selections screen enables you to select components from a directory and the HP FTP site (ftp://ftp.hp.com) (for HP ProLiant servers and selected options only) as a location for obtaining updates to your systems. You can also select components that have already been downloaded. You can use up to all three of the methods simultaneously.
|
NOTE: For offline deployments, the Source Selections screen does not appear. |
|
NOTE: HP SUM does not support the ability to download the latest components from ftp.hp.com to HP Integrity servers. |
For HP ProLiant servers, the following screen appears when selecting the location to check for updates.
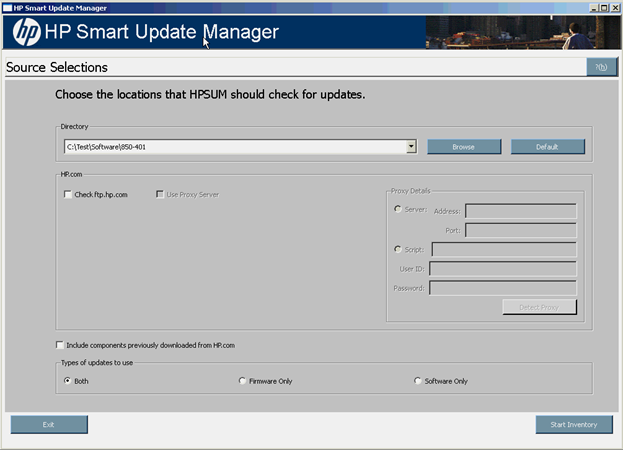
When using HP SUM delivered with the Integrity support pack, the following screen appears when selecting the location to check for updates, since HP SUM does not support the ability to download the latest components from ftp.hp.com for these servers.
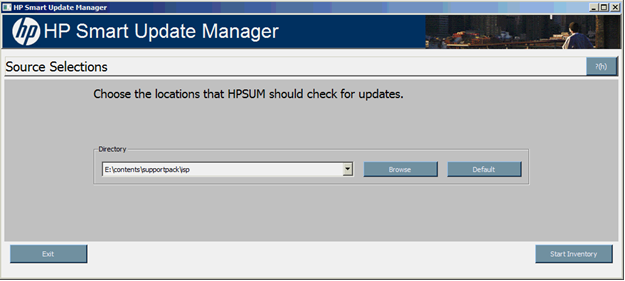
The Source Selections screen enables you to specify where to get components for updating the targets by using one or more of the following methods:
- Directory - This field enables you to select the directory where the components you want to deploy are located. It can be located on a locally accessible file system. The default location is the directory from where HP SUM is executed. To change the directory value, click Browse to launch a select-directory menu. To set the field back to the initial value, click Default.
- Check ftp.hp.com - (Only for HP ProLiant servers) Select this checkbox to get firmware and software components located on the HP FTP site (ftp://ftp.hp.com). The HP FTP site contains the latest versions of the firmware and software components available from HP. The components, which are applicable (denoted with an HP.com icon) are available for selection on the Select Items to be Installed screen. When using this method, both firmware and software components are available for selection depending on the options set on the Set Bundle Filter screen when PSPs or bundles are included in the components to be deployed. To limit only the appearance of available firmware components, use the /romonly command-line argument and use the /softwareonly command line argument for software components. The components are not downloaded from the HP FTP site to a target until the Install button is actually selected unless the component is required to discover supported devices. If components are required for discovery, then you are prompted to allow this action. If components are already up-to-date, the components do not appear.
- The Check ftp.hp.com (only for ProLiant servers and select options) checkbox is cleared by default. To receive updates from the web, select the Check ftp.hp.com checkbox. To use a proxy server and enable the proxy details group box, select the Use Proxy Server checkbox.
- Proxy Details - Enter the proxy information in the Proxy Details group box to be used to access the HP FTP site. To auto-detect the proxy information, click Detect Proxy. If you use a proxy server in accessing the HP FTP site, the proxy information is saved and prepopulated on the next deployment.
| NOTE: HP SUM does not support FTP over HTTP proxy. |
| NOTE: FTP downloaded from HTTP proxy fails. Components from the HP FTP site are only presented for selection on the Select Items to Install screen if their versions are newer than what is already on the system. If a system has all of the latest versions of firmware and software, no components from HP.com are presented on the Select Items to be Installed screen.
|
| NOTE: HP SUM does not support the ability to download the latest components from ftp.hp.com to HP Integrity servers. |
- Include components previously downloaded from HP.com-This option includes the components that have been previously downloaded from the HP FTP site as available for selection on the Select Items to be Installed screen. The default location for the previously downloaded components is %TEMP% \hp_sum\RepositoryManager\Repxx\<component_number> directory. To use components already downloaded from the HP website, select this checkbox.
To begin the inventory process, click Start Inventory. The Inventory Progress screen appears while the HP SUM builds an inventory of available updates.
Download Permission (applicable only for ProLiant servers)
Before starting any discovery, HP SUM searches the web digest for self-discovery components that must be downloaded for the discovery process. Self-discovered components are components including but not limited to NIC firmware and tape firmware that HP SUM uses to discover the hardware in the system. If the Check ftp.hp.com checkbox has been selected on the previous screen, then the Download Permission screen might appear if there are self-discovery components that are available for download.
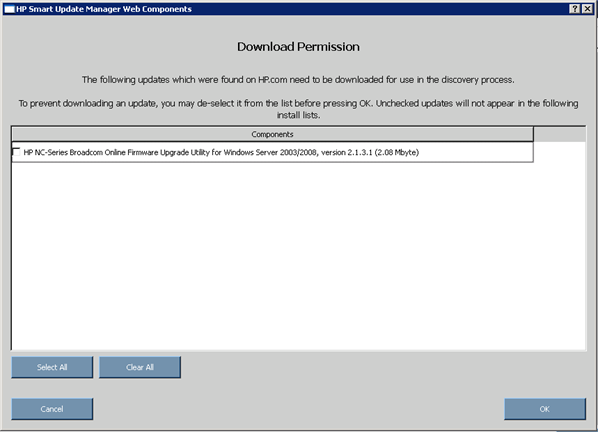
The Download Permission screen lists the available self-discovery components found on the HP FTP site. You can select or clear the updates you are downloading. The Download Permission screen includes the following buttons:
- Select All - Selects all available components for download.
- Clear All - Clears all components selected for download.
- Cancel - Exits the Download Permission screen and returns to the Source Selections screen.
- OK - Downloads all selected components.
| NOTE: Emulex HBAs, QLogic HBAs, Brocade HBAs, and offline-only components cannot be retrieved from the HP website and can only be installed offline. These components do not appear on the web components list.
|
For more information on selecting the location for updates, see Selecting the location to check for updates.
Selecting an installation host
To continue with the deployment process using a local host, select a host from the Select Installation Host(s) screen, and then click Next.
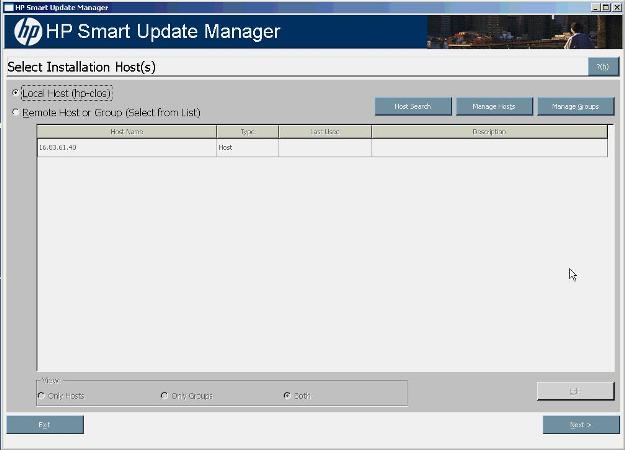
The Select Installation Host(s) screen enables you to choose a host for component installation. By default, the first time you run HP SUM on a particular system, the only host available is the local host. However, you can also select remote hosts as your targets. For more information about using the GUI for multiple remote deployments, see "Multiple-host installations"
The following columns are included in the Select Installation Host(s) screen:
- Host Name - Displays the host IP address or DNS name.
- Type - Categorizes the system as a host or group.
- Last Used - Enables you to sort the list by the most recently used hosts.
- Description - Displays the user-defined description given to a host.
When the Remote Host or Group option on the Select Installation Host(s) screen is selected, you can sort your view of the host list by selecting Only Hosts, Only Groups, or Both.

The Select Installation Host(s) screen also includes the following buttons:
- Host Search - Enables you to search for remote hosts using the following options
- Ping Scan for Remote Hosts
- Port Scan for Remote Hosts
- LDAP Query for Remote Hosts
- Onboard Administrator scan for iLO Hosts

- Manage Hosts - Enables you to add, edit, and delete hosts.
- Manage Groups - Enables you to add, edit, and delete groups.
- Edit - Enables you to edit the selected host.
- Next - Proceeds to the next step in the installation process where the local or remote system checks for already installed items.
- Exit - Exits HP SUM.
|
NOTE: When running on a Linux system and the expect-5.x package is not installed, HP SUM displays a pop-up error message reporting that the package is missing and you are not able to deploy to remote systems. However, you can still deploy to the local host. To perform a remote deployment, exit HP SUM, and then install the expect-5.x package from the Linux operating system media. To proceed with remote deployment, start HP SUM.
|
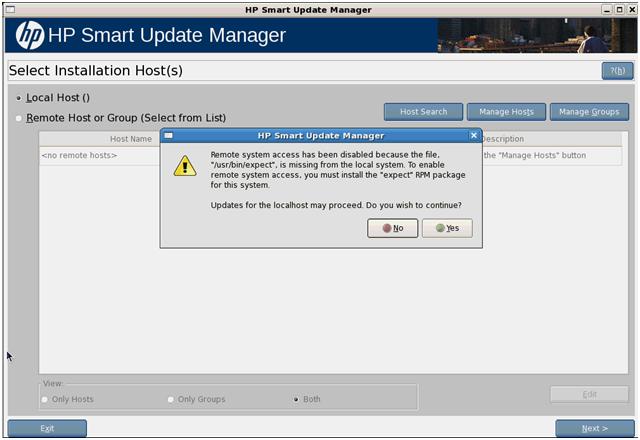
To continue to system discovery, click Next and the discovery process occurs. If the system discovery process finds one or more predefined bundles, the Select Bundle Filter screen appears.
Selecting bundles to filter
When the discovery process is complete and there is a bundle in the repository, the Select Bundle Filter screen appears. The Select Bundle Filter screen displays information about the predefined bundles available on your system and enables you to select which bundles to install. This screen also enables you to set options for non-bundle product versions. If you specify a bundle on the command line when starting HP SUM, this screen does not appear.
The Select Bundle Filter screen is divided into two sections.
The upper part of the screen includes the product and status information:
- Product - Displays the product name of the predefined bundles found on the system. It also provides information about available versions.To view the bundle version history, click the version number in the Product column. To view the bundle contents, click View Contents.
- Status - Indicates whether the installation is ready to proceed. It also provides additional information about the contents of the identified bundles. To view the list of components that are in the repository associated with the bundle, click the <number of> Components Found link. To view the list of components associated with the bundle missing from the repository, click the <number> Missing link. You can obtain the missing components from the source media or from the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
The following image illustrates the Select Bundle Filter screen.
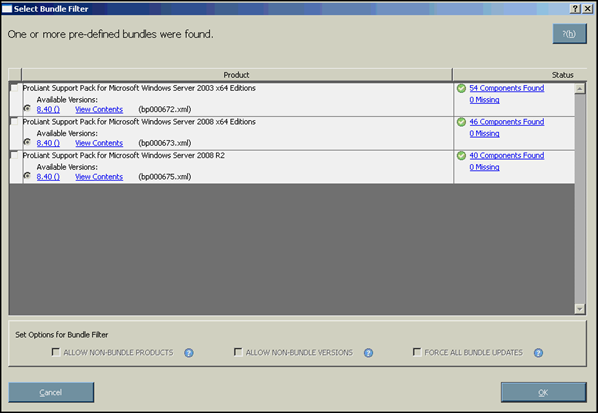
The Set Options for Bundle Filter section allows you to set options for non-bundle product versions.
- To view all versions of the products included in the bundle, select ALLOW NON-BUNDLE VERSIONS. This option enables you to include updates that might be newer than those released in the bundle.
- To view updates of products not included in the bundle, select ALLOW NON-BUNDLE PRODUCTS. This option enables you to update other components on your system as you apply the bundle.
- To force the installation process on the bundle products, select FORCE ALL BUNDLE PRODUCTS. This option enables you to install bundle products when the installed version is the same as or newer than the components in the bundle. This enables the installed software to be downgraded.
To proceed with the deployment process, click OK.
|
NOTE: If a PSP, ISP, or bundle that supports the target's operating system is not present in the repository, HP SUM might display a message box indicating that a supported bundle is not present in the repository. |
Selecting components to install
When the discovery process is complete and a bundle has been selected, the Select Items to be Installed screen appears. The Select Items to be Installed screen displays information about which components are available for installation on your system and enables you to select or clear components to install.
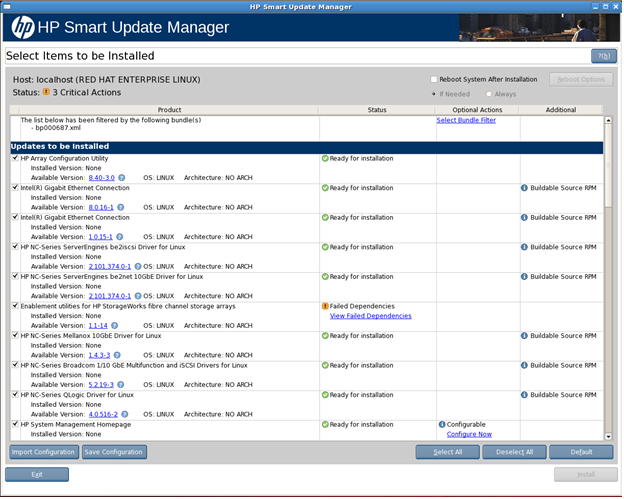
The Select Items to be Installed screen includes the following sections:
- Host - Lists the system on which the selected items are installed.
- Status - Indicates if the installation is ready for installation.
- Reboot section - Enables you to specify reboot settings and determine when reboots occur.
- Component selection pane - Enables you to specify which components to install.
When updating installation for some but not all NIC firmware components, select the devices to be updated in the window that appears. If the NIC firmware listed for the device does not have a version, you cannot add that firmware to the device using HP SUM.
When multiple hardware devices such as hard drives or array controllers exist in a single server, HP SUM lists each device only one time. If the devices have different firmware versions, then the versions are listed from earliest to latest in a range. When multiple instances of the firmware are available for installation, the instances are listed from latest to earliest. If necessary, all hardware device firmware is flashed to the selected version.
The Select Items to be Installed screen also includes the following buttons:
- Select All - Selects all available components for installation.
- Deselect All - Clears all components selected for installation.
- Default - Restores the selections in the product installation pane to the default view, which is based on the existing configuration of the local system.
- Exit - Exits HP SUM.
- Install - Installs all selected components.
- Import Configuration (Linux RPMs only) - Provides the option to import the configuration file.
- Save Configuration (Linux RPMs only) - Provides the option to save the configuration file on the local system.
The Select Bundle Filter screen can be opened from the Select Items to be Installed screen by clicking the Select Bundle Filter link in the Optional Actions section.
The component selection pane in the Select Items to be Installed screen is divided into sections, which might vary depending on your system. These sections include the following headings:
- Deselected By User - You have deselected the components in this section, and the components are not installed.

- Installation Not Needed - The components in this section do not need to be updated, but can be. To update the components, select the components, and then click Installation Options.

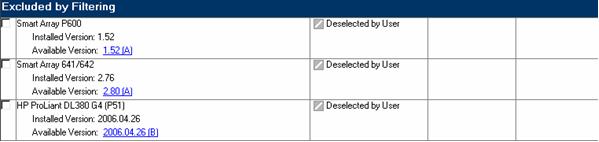
- Excluded by Filtering - The components in this section were excluded through your filtering options. You can use the Select Bundle Filter option or one of the command line arguments, /romonly or /softwareonly, to change the exclusion on a single target. For multiple targets, this must be repeated on each additional target. The Select Bundle Filter option screen is only available when bundles such as support packs are included in the location where the components to be downloaded are.
|
NOTE: A common way to view this section is if multiple versions of a component in a repository exist and one version of the component is in the bundle that has been selected to be used. If you do not select Allow Non-bundle versions on the Select Bundle Filter screen, the additional component versions display in this section. |
- Updates to be Installed - The components in this section can be installed on your system.
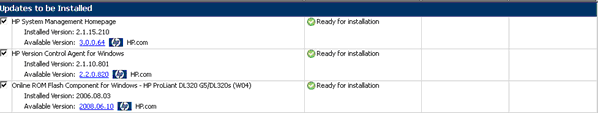
- Optional Updates - The components in this section are not selected for installation by default, even if the product is not already installed or is installed but not up-to-date. To include the component in the installation set, you must select the component.

- No Device Driver Installed - The devices supported by the components in this section are detected on the system, but HP Smart Update Manager requires a device driver before the component can be made available for installation. Install the device driver.

Multi-session installation appears on the Select Items to be Installed screen under certain combinations of dependencies between the components selected for installation.
- Component B depends on the product in component A, in a manner that requires the product to be already installed and active for component B to install.
- Component A requires a reboot after installation to become active.
- A version of the product in component A is not already installed or the version is not one of the correct versions to satisfy the dependency.
If all of the previous conditions are true, then HP SUM detects it and a notification to reboot appears to continue the installation. All installable components appear in the original update list, but only the components shown before the notification are installed. You must reboot to complete the installation and then restart HP SUM to continue the installation process.
Status field

The Status field of the Select Items to be Installed screen displays information about whether the installation is ready to proceed or not.
| Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Ready |
All selected components are ready to be installed. |
 |
Already up-to-date |
No component installation is required. |
 |
None Selected |
No components are selected for installation. |
 |
x Critical Action |
X components are not ready for installation due to failed dependencies, where x is the number of components. The installation cannot proceed until the dependencies are met or the component is deselected for installation. |
Reboot section
The reboot section of the Select Items to be Installed screen enables you to specify preferred reboot behavior.

To instruct the system to reboot after updates are installed:
- Click Reboot System After Installation.
- Click Always or If Needed.
When Always is selected, then the system will always be rebooted unless there is a component installation failure. When If Needed is selected, then the system will be rebooted if needed by at least one component, unless there is a component installation failure.
To change the delay before reboot or the reboot message, click Reboot Options. The Set Reboot Options screen appears.

|
NOTE: In Linux, the Reboot Delay time is automatically converted from seconds to minutes. Any value under a full minute, 59 seconds or less, will be rounded to the next minute for Linux.
|
Make any changes, and click OK.
|
NOTE: The reboot options do not apply when deploying firmware to HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers with HP SUM. HP SUM will reboot the server automatically during the firmware update process when the user has selected Upload and Activate. Checking any other reboot options or setting a reboot delay is not applicable
|
Component selection pane
The component selection pane of the Select Items to be Installed screen displays (by component number order, unless a dependency causes the installation order to change) components available for installation based on your server and hardware options. HP SUM verifies each component for dependencies, if the component is already installed on the system, or if it requires a reboot after installation. Items available for installation are selected by default. You can deselect any components you do not want to install.
The component selection pane is divided into the following columns:
- Product - Specifies the name of the component, version number, new component version number, and the criticality status of the component updates. To view the component version history, click the new version number. If a component is retrieved from ftp.hp.com, it has an HP icon next to it. For Linux RPMs, the operating system and system architecture are listed.
| Criticality Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Critical |
HP requires users to update to this component version immediately. |
 |
Recommended |
HP recommends that users update to this component version at their earliest convenience. |
 |
Optional |
Update to this component version if their system is affected by one of the documented fixes or if they want to utilize any of the enhanced functionality provided by this version. |
 |
Unknown |
Component status is not available. |
NOTE: All Linux RPMs have the Unknown criticality icon  , because the RPM update information is not available to HP SUM. , because the RPM update information is not available to HP SUM.
|
- Status - Displays the status of the component.
| Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Ready for installation |
The component is ready for installation. |
 |
Not selected for installation |
The component has not been selected for installation. |
 |
Already up-to-date |
The component is already up-to-date. To downgrade or rewrite a component, click Installation Options. |
 |
No device driver installed |
The firmware devices supported by the components in this section are detected on the system but require a device driver. Install the device driver. |
 |
Deselected by user |
The component has not been selected for installation. |
 |
Excluded by Filtering |
The components excluded which are not applicable to the target server. |
 |
Failed dependencies |
The component has a dependency that has not been met. To determine the nature of the failed dependency, click View Failed Dependencies. |
 |
Build Failed |
The component build has failed. To view the Build.log, click the View build log link. |
- Optional Actions - Indicates whether the component configuration is optional or required but has already been updated.
- Additional - Shows additional information for the components if required. Examples include links to installation options, buildable source RPMs, non-bundle products, and so on.
|
NOTE: For Linux source RPMs, if the source packages are not installed, then the source RPMs are not available for selection. To deploy any Linux source RPMs, ensure that the appropriate source packages are installed before starting HP SUM.
|
|
NOTE: When deploying source RPMs, the Linux operating system, including the kernel on the system running HP SUM, must be the same as the system that the resulting RPM will be deployed to.
|
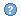
If a component displays as Build Failed, you must resolve the issue before proceeding with the installation.

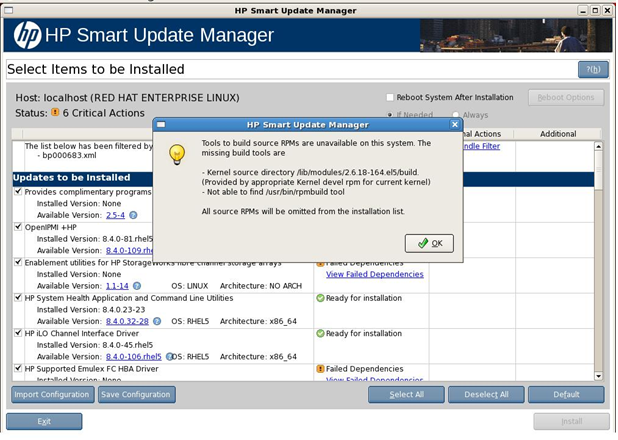
If a failed dependency occurs, then you must resolve it by ensuring the prerequisite libraries or the appropriate software or firmware components are available before proceeding with the installation.
The following figure displays the Failed Dependencies screen.
Installation options
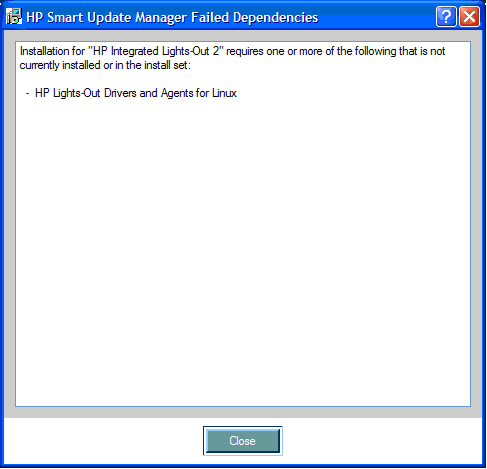
You can specify firmware upgrade behavior for installable components by selecting one or more options from the Additional Options field.
 CAUTION: Updating the firmware while a shared device is in use can lead to data loss. Before enabling the Allow Shared Devices option, be sure any other servers sharing the selected devices are offline. CAUTION: Updating the firmware while a shared device is in use can lead to data loss. Before enabling the Allow Shared Devices option, be sure any other servers sharing the selected devices are offline.
|
- Select Allow Downgrades to downgrade the current firmware to an older version.
- Select Allow Rewrites to enable HP Smart Update Manager to overwrite the current firmware version with the same version.
- Select Allow Shared Devices to upgrade firmware in a shared storage environment.
|
NOTE: HP Smart Update Manager does not support Allow Downgrades or Allow Rewrites for the HP Virtual Connect Ethernet and Fibre Channel Modules for c-Class BladeSystem firmware component.
|
The following table illustrates how changing the options for firmware upgrade behavior changes the firmware upgrade results. In this example, the array controller is assumed to be an HP Smart Array 6402 controller.
If the existing array controller has firmware version 3.00 installed, then updating the firmware produces the following results.
|
Default |
Allow downgrades |
Allow rewrites |
| Firmware upgrade v3.05 |
3.05 |
3.05 |
3.05 |
| Firmware upgrade v3.10 |
3.10 |
3.10 |
3.10 |
If the existing array controller has firmware version 3.10 installed, then updating the firmware produces the following results.
|
Default |
Allow downgrades |
Allow rewrites |
| Firmware upgrade v3.05 |
No change |
3.05 |
3.10 |
| Firmware upgrade v3.10 |
No change |
No change |
3.10 |
|
NOTE: When updating installation for NIC components, select the devices to be updated in the window that appears.
|
After you have selected all the components that you want to install, click Install to proceed with the installation. The Installation Progress screen appears.
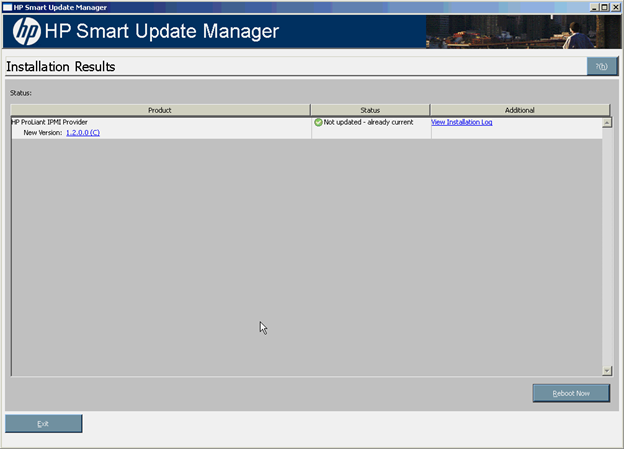
Viewing the installation results
When the installation is complete, the Installation Results screen appears.
The Installation Results screen is divided into the following columns:
- Product - Specifies the name of the installed component. To view the component version history, click the version number.
- Status - Specifies the installation status of the component.
The following icons might appear in the Status column.
| Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Success |
The component was installed successfully. |
 |
Same/older version successfully installed |
The existing component was successfully downgraded or reflashed to the same or older version. |
 |
Update returned an error |
An update error has occurred. For details, see the HP SUM log file. |
 |
Installation failed |
The component was not installed. To see additional details, click View Installation Log. |
- Additional - Enables you to view the installation log for each component and reminds you if a reboot is required.
| Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Reboot Needed |
The server must be rebooted for the component to take effect. |
To view the installation result details, click View Installation Log.

The Installation Results screen also includes the following buttons:
- Reboot Now - Reboots the server. (This button is available for local installations only.)
- Exit - Exits HP SUM.
|
NOTE: After updating hard drives in external enclosures such as MSA20, you must power cycle the external enclosures. The Reboot button in HP Smart Update Manager only reboots the server but never power cycles an external enclosure.
|
The following installation logs contain information about the installation activity for each host being updated:
- hpsum_log.txt log - Contains a brief summary of the installation activity
- hpsum_detail_log.txt log - Contains all of the installation details, including errors, for each component installed
The log files can be found in the following locations:
- For Windows operating systems, these files are located in subdirectories named according to the IP address of each host in the \CPQSYSTEM\hp\log subdirectory on the boot partition of the local host. The directory containing the local host information is named localhost instead of being named after the IP address.
- For Linux operating systems, these files are located in subdirectories named according to the IP address of each host in the /var/hp/log subdirectory of the local host. The directory containing the local host information is named localhost instead of being named after the IP address.
A new file contains detailed information on the execution of HP SUM.
- For Windows operating systems, the filename is: C:\cpqsystem\hp\log\hpsum_execution_log_<date>_<time>.log
- For Linux operating systems, the filename is: /var/hp/log/hpsum_execution_log_<date>_<time>.log
|
NOTE: Using the offline environments provided by the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD and HP BladeSystem Firmware Deployment Tool results in the log files being written to the Linux location.
|
HP SUM also creates trace logs of its installation that can be used to debug problems. These trace files are located in the following places:
- For Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, and Windows Vista - %TEMP%\hp_sum\
- For Windows Server 2008 and Windows Microsoft Windows Server 2011 Small Business and 2011 SBS Essentials - %TEMP%\<number>\hp_sum
- For Linux - /tmp/hp_sum
HP SUM creates a separate trace log for each target server. These are captured in subdirectories under the trace log directories. The directories start with Target_0, Target_1, and so forth. These contain the target specific trace information. No passwords or sensitive data is stored in this trace logs.
Multiple-host installations
HP SUM provides simultaneous firmware and software deployment for multiple ProLiant remote targets and options in both GUI and CLI modes. For performance and optimization, if more than 20 remote targets exist for simultaneous update, HP SUM starts with the update for the first 20 targets and when each target update completes, then the next target in line is selected until all targets have been updated.
After you start HP SUM, the Source Selection screen appears, enabling you to specify where to find the components that you want to deploy. After selecting the component's location, the Inventory Progress screen appears while HP SUM builds an inventory of available updates. When the inventory process is complete, the Select Installation Host(s) screen appears.
Selecting remote hosts or groups
The Select Installation Host(s) screen enables you to choose multiple hosts and groups for component installation. A remote host can be the IP address or DNS name of a remote server, remote iLO NIC port, Virtual Connect Ethernet or Fibre Channel Module for c-Class BladeSystem, or BladeSystem Onboard Administrator.
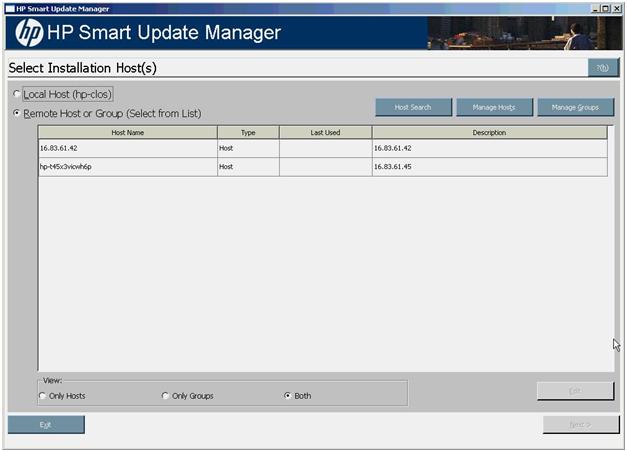
To search for remote hosts, see "Searching for remote hosts" To add hosts, see "Managing hosts." To add groups, see "Managing groups."
To continue with the deployment process:
- Select one or more hosts or groups.
- To continue, click Next.
- Enter the credentials for the host.
- Click OK to proceed, as described in Selecting components to install on multiple hosts.
- When the installation is complete, the Installations results for multiple hosts screen appears.
|
NOTE: When running on a Linux system and the expect-5.x package is not installed, HP SUM displays a pop-up error message reporting that the package is missing and you are not able to deploy to remote systems. However, you can still deploy to the local host. To perform a remote deployment, exit HP SUM, and then install the expect-5.x package from the Linux operating system media. To proceed with remote deployment, start HP SUM.
|

Searching for remote hosts
The Host Search button enables you to search for hosts in the network using the following options:
- Ping Scan for Remote Hosts - This option is used to search for hosts using an IP address range.
- Port Scan for Remote Hosts - This option is used to search for hosts using the IP address range along with the Ports to Scan.
- LDAP Query for Remote Hosts - This search option uses the LDAP server information to retrieve servers in that network.
- Onboard Administrator scan for iLO Hosts - This option is used to search for hosts using their iLO IP address.
Managing hosts
To add, edit, or delete hosts, click Manage Hosts. The Manage Hosts screen appears. A remote host can be the IP address or DNS name of the following:
- Remote server
- Remote iLO NIC port
- Virtual Connect Ethernet or Fibre Channel Module for c-Class BladeSystem
- BladeSystem Onboard Administrator
- Interconnect switch - 3 GB SAS BL Switch
|
NOTE: Local hosts cannot be included in a list with remote hosts or in a group. When selecting iLO and iLO 2 for ProLiant, iLO 3 for ProLiant and Integrity, OA, VC, or 3 Gb SAS BL Switch for ProLiant as a target, only the firmware component for that particular hardware can be updated. The server host must be selected to update all other firmware and software components. The iLO firmware can be updated by either selecting the iLO version or the server host.
|
|
NOTE: An LO-100 BMC IP cannot be used as a target to update the LO-100 firmware directly. If used, the following pop-up message displays: Could not contact host. You can only update the LO-100 firmware when updating firmware on a 100-series server.
|

To add a host:
- Click Add Host. The New Host dialog box appears.

- Select the method to add a host from the following:
- Enter the DNS name of the host you want to add.
- Enter the IP address of the host you want to add.
- Enter the IP address range of the hosts you want to add. The starting and ending IP addresses must both be on the same subnet. When using the IPv6 format, the last field in the ending address is limited to 32 targets.
|
NOTE: When adding hosts using either IP address option, you can select from the IP format options: IPv4 or IPv6. The IPv4 format is the default option since it is the current Internet protocol. The IPv6 format is the next generation Internet protocol.
|
- Enter an optional user-defined description given to the host you want to add.
- Click OK.
The new host is added to the list on the Select Installation Host(s) screen.
To edit an existing host:
- On the Manage Hosts screen, click Edit Host. The Edit Host dialog box appears.

- Edit the Host Name and Description.
- Click OK.
To delete a host:
- On the Manage Hosts screen, click Delete Host.
- When the confirmation screen appears, click Yes.

Managing groups
To add, edit, or delete groups, click Manage Groups. The Manage Groups screen appears.

To add a group:
- Click Add Group. The Edit Group dialog box appears.

- Enter a group name.
- Enter an optional user-defined description given to the group to be added.
- Select the hosts to be added to the group from the Available Hosts pane. You can add new hosts from this screen by clicking New Host. For more information on adding hosts, see "Managing hosts."
- Click Enter to move the selected hosts to the new group.
- Click OK.
The new group is added to the list on the Select Installation Host(s) screen.
To edit an existing group:
- Select the group, and then on the Manage Groups screen, click Edit Group. The Edit Group dialog box appears.

- Edit the group name as needed.
- Edit the optional user-defined description given to the host as needed.
- Click Enter and Remove to add or remove hosts as needed.
- Click OK.
To delete a group:
- Select the group on the Manage Groups screen, and then click Delete Group.
- When the confirmation screen appears, click Yes.
Entering credentials for hosts
When you select a single remote host, the Enter Credentials for Host screen appears. You must enter your username and password as the credentials for the host.

To enter the credentials for the host, choose one of the following:
- Select Enter Username and Password, and then enter the username and password.
- Select Use Current Credentials to use the credentials of the user currently logged in.
This option is for Windows operating systems only. Selecting Use Current Credential requires an existing trust relationship with the host. When this option is selected, the credential of the current user credential is used to login to the remote host.
|
NOTE: When deploying components to non-server targets, you cannot use the Use Current Credentials option since it is not possible to share credentials between a system and a non-server target.
|
If an active update process is detected on the remote host, you can select Skip host or Restart update.
- Skip host - Causes the host to be ignored for the rest of the update process
- Restart update - Causes any existing or in-progress installation to be terminated
To continue, click OK.
|
NOTE: When deploying components to Windows operating system targets, you might be required to enter the username in DOMAIN\USER format, where <user> is the user account name and <domain> is the computer name or active directory domain of the user account. |
When you select a group or multiple hosts, the Enter Credentials for Group screen appears.
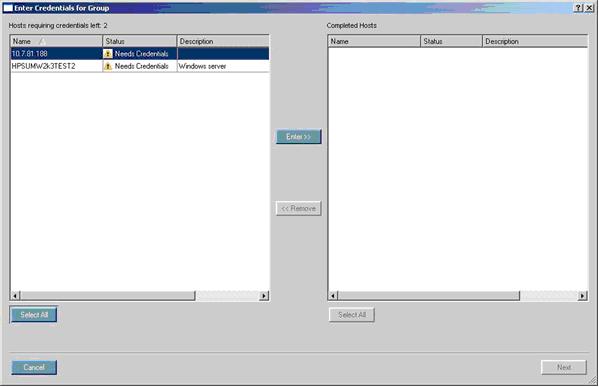
The screen separates the remaining hosts that still require credentials from the completed hosts.
Each pane is divided into the following columns:
To enter the credentials for the host, perform the following steps:

- In the left pane, select the host from the list of hosts requiring credentials. If all credentials are the same, to select all the hosts on the list, click Select All.
- To enter the required credentials and move the selected host to the Completed Hosts pane, click Enter.
- To continue, click Next.
|
NOTE: If a TPM is detected and enabled, an HP Smart Update Manager pop-up warning message appears after the Discovery Progress screen. You must read the message and determine how to proceed. For more information, see Trusted Platform Module.
|
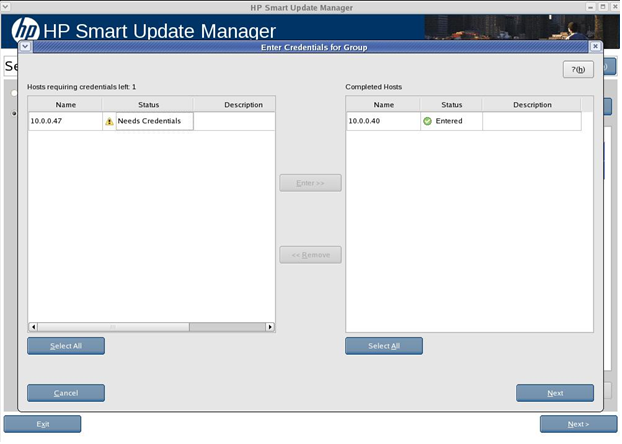
Selecting bundles to filter on multiple hosts
If the system discovery finds one or more predefined bundles, the Select Bundle Filter screen appears. If you specify a bundle on the command line when starting HP SUM, this screen does not appear.

For more information about the screen, see "Selecting bundles to filter." To proceed with the installation process, click OK.
Selecting components to install on multiple hosts
The Select Items to be Installed screen displays the server hosts and the status information.

The Select Items to be Installed screen includes the following buttons:
- View Host - Enables you to view additional information about a host after you select it.
- Install - Installs all selected components on all remote hosts. The Install button is grayed out when a dependency failure occurs.
- Exit - Exits HP SUM.
The server host pane of the Select Items to be Installed screen displays summary information for the server hosts available for installation and features a drilldown of individual hosts.
The server host pane is divided into the following columns:
- Host - Specifies the name of the system, number of updates available, and the estimated time for the installation.
- Status - Specifies the status of the host.
| Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Ready |
The host is ready for installation. |
 |
Nothing to Install |
The host is already up-to-date. |
 |
Host Skipped Due to Existing HP SUM Session |
The host is skipped due to an existing HP Smart Update Manager session. |
 |
Action Required |
The host is not ready for installation. Click View Host for additional information. |
 |
Discovery Failed |
The host is not ready for installation. The detection of installed hardware, software, and firmware has failed. |
|
NOTE: The default reboot behavior after updates are installed might also appear in the Status column.
|
To zoom in to single host selections, click View Host on the Select Items to be Installed screen. The Selections for Single Host screen appears.

To set single-host selections, proceed as described in "Selecting Components to Install."
After setting the single-host selections for all hosts to be updated, on the Select Items to be Installed screen, to proceed with the installation, click Install.
Updating Firmware on HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers
One firmware package for the HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers includes System Firmware which requires a reboot to activate the firmware. To specify this, the user can select the Configure Now link to select one of the following options:
- Upload and Activate - (Default selection). If you select this option, after the component is uploaded to the server which is up and running, HP SUM shuts down and restarts the server to activate the system firmware immediately.
- Upload but Do not Activate - If you select this option, the firmware is activated the next time the server is rebooted.
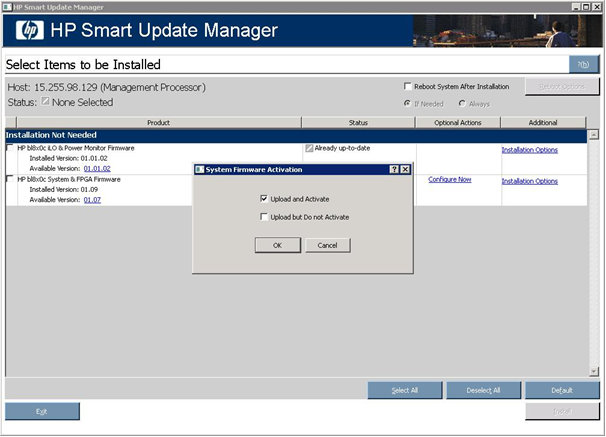
If the user has not changed the default option or has selected Upload and Activate, a warning message displays, indicating that HP SUM will reboot the server during the firmware update process.

To continue the update, press OK.
You can deploy the Online System, FPGA, iLO-3 MP and Power Monitor firmware using CLI in silent mode. However, you cannot specify the Upload and Do not Activate mode using CLI. Only the default Update and Activate mode is available and no parameter is required.
Viewing the installation results for multiple hosts
When the installation is complete, the Installation Results screen appears.
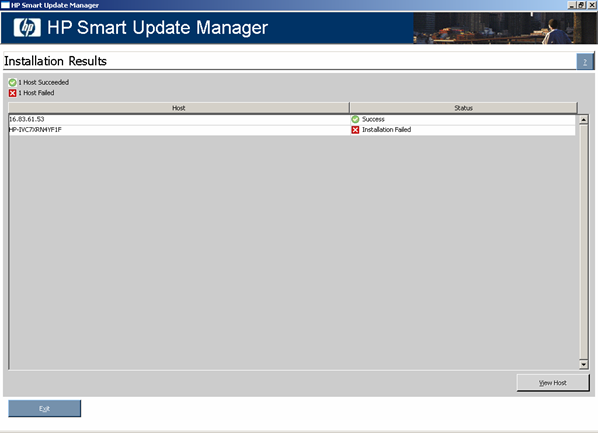
The Installation Results screen is divided into the following columns:
- Host - Specifies the IP address or DNS name of the host.
- Status - Specifies the overall installation status of the components on the remote host.
| Icon |
Text |
Description |
 |
Success |
The host was updated successfully. |
 |
Nothing to install |
The host is already up-to-date. |
 |
Installation canceled by user |
The installation was canceled and cannot continue the process. |
 |
Installation failed |
One or more of the component installations have failed.
|
The Installation Results screen also includes the following buttons:
- View Host - Enables you to view the installation results for the selected host.
- Exit - Exits HP SUM.
To view single-host installation results, double-click or select the host, and then click View Host.
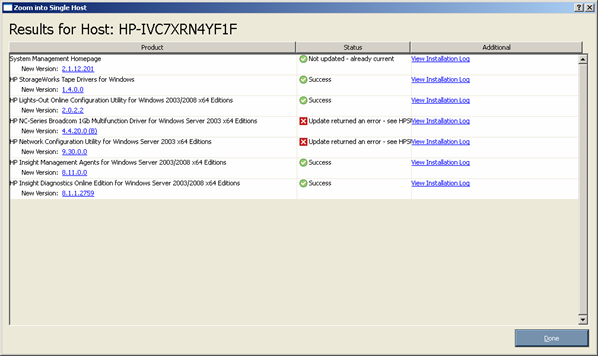
Proceed as described in Viewing the installation results.
Scripted deployment
In this section;
Command-line interface
Return codes
Input files
Command-line usage of input file
Input file format and rules
File Encoding
Error Reporting
Input file parameters
Deploying firmware and software simultaneously
Reports
Command-line interface
The HP SUM command-line interface enables you to script custom installations.
Command-line syntax
The general command-line syntax for HP SUM is:
hpsum [/h[elp]] [/?] [/f[orce]] [/f[orce]:bundle] [/f[orce]:rom] [/f[orce]:software] [/f[orce]:all ] [/g (/downgrade)] [/e (/rewrite)] [/m[utual])] [/c[omponent] <component_to_install>] [/s[ilent]] [/allow_update_to_bundle] [/allow_non_bundle_components] [/b[undle] <bundle_to_install>] [/express_install] [/use_snmp] [/use_location "file_share"] [/use_web] [use_proxy] [proxy_server] [/use_d[ownloaded]*] [/tpmbypass] [/ignore_tpm] [/use_wmi] [/use_latest] [/romonly] [/softwareonly] [/continue_on_error <error>] [/override_existing_connection] [/On_failed_dependency:<Parameter>] [/r[eboot]] [/reboot_message "reboot message"] [/reboot_delay timeout_in_seconds] [/reboot_always] [/dryrun] user <username> or /username <username>] [/passwd <password>] [/current_credential] [/target "netAddress"] [/group "group_name"] [/ [/logdir "path"] [/v[erbose]] [/veryv[erbose]] [/report] [/inventory_report] [/firmware_report] [/inputfile "filename"] [/deleteinputfile "filename"][<component1_to_install> <component2_to_install> ...] [<bundle1_to_install> <bundle2_to_install> ...]
HP SUM with Onboard Administrator requires a user ID and password to log in. The user ID must be an Administrator equivalent ID and not an operator or user equivalent level ID.
|
NOTE: All arguments and information enclosed in brackets are optional. The arguments may be prefixed with either a '-' or '/' character. These examples show only the '/'.
|
On Windows operating systems, use a slash (/) before each argument. On Linux operating systems, use a hyphen (-) before each argument.
If the /s[ilent] argument is not included on the command line, the HP SUM GUI appears.
|
NOTE: Command line syntax does not support double-byte character sets. Any messages entered through the command line using a double-byte character set will not be displayed correctly.
|
|
NOTE: When using HP SUM with HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Server bundles, HP SUM does not have any command-line arguments to specify the Upload and Do Not activate option. If HP SUM is started from the command line using the silent argument (/s[ilent]), then the system being updated reboots automatically. Also, no reporting functionality using CLI is available when using HP SUM for firmware updates on these servers.
|
Command-line arguments
HP SUM recognizes the following command-line arguments. These arguments prepopulate the GUI in the Select Items to be Installed screen. If you specify the host or group, then the Select Items to be Installed screen does not appear.
You cannot use some arguments, such as /romonly and /softwareonly together.
| Command-line argument |
Description |
| HELP |
| /h[elp] or /? |
This argument displays command line Help information. |
| INSTALLATION OPTIONS |
| /f[orce] |
This argument enables you to override or downgrade an existing component installation. This argument produces the same results as /f:software. |
| /f[orce]:bundle |
This argument enables you to override or downgrade the existing installation of components in the selected bundle. |
| /f[orce]:rom |
This argument enables you to override or downgrade the existing installation of the selected firmware components. (Applies to firmware only.) |
| /f[orce]:software |
This argument enables you to override or downgrade the existing installation of the selected software components. |
| /f[orce]:all |
This argument enables you to override or downgrade the existing installation of the selected software components, firmware components, and bundles. |
| /g or /downgrade |
This argument enables you to downgrade to an earlier version of firmware for multi-target devices such as hard drives and array controllers. (Applies to firmware only.) |
| /e or /rewrite |
This argument enables you to rewrite the same version of firmware only for multi-target devices such as hard drives and array controllers. (Applies to firmware only.) |
| /m[utual] |
If the device you want to flash is in a shared storage environment, then this argument informs the firmware flash engine to flash the firmware.
If the device to be flashed is in a shared storage environment, and the /m option is not passed, then the component installation fails. (Applies to firmware only.) |
/c[omponent]
<component to install> or <component1_to_install> <component2_to_install> |
This argument specifies the components to install. Components to install can be specified with or without the /c[omponent] argument.
If using the /c[omponent] argument, then only one component can be specified with the argument. However, multiple /c arguments and components can be specified on the same line.
If the /c[omponent] argument is not used, then multiple components can be specified at the same time, but the components must be separated by a blank and listed after all the arguments on the command line.
The components are installed in the order provided unless dependencies between components require installation in a different order. If so, the utility changes the installation order based on the component dependencies to ensure the successful installation of as many components as possible.
Multiple components and bundles can be specified on the same command line. When mixing components and bundles on the command line, the filter switches control what components and bundles are installed. |
| /s[ilent] |
This argument causes the installation to run silently with no GUI or console output. All data writes to the log file. Any generated prompts use the default option and continue the installation without user input. If a component requires input before installation (such as configuration information), then the component installation fails, and an error message writes to the log file.
Failed dependencies are not reported to the user when using the /s[ilent]argument. To check for failed dependencies, remove the /s[ilent] argument, reissue the command line, and then the HP SUM GUI appears. |
| /allow_update_to_bundle |
This argument is a filter switch and enables the user to install newer versions of components defined in a PSP, ISP, or firmware bundle. This argument enables these components to replace the older versions of the same component that might have shipped with the bundles. |
| /allow_non_bundle_components |
This argument is a filter switch and enables the user to install components that are not included in the bundle but reside in the directory with the components in the bundle. |
| /b[undle] <bundlename> or <bundle1_to_install> <bundle2_to_install> |
This argument specifies the bundles to install. Bundles to install can be specified with or without the /b[undle] argument.
If using the /b[undle] argument, then only one bundle can be specified with the argument. However, multiple /b arguments and bundles can be specified on the same line.
If the /b[undle] argument is not used, then multiple bundles can be specified at the same time, but the bundles need to be separated by a blank and listed after all the arguments on the command line.
Multiple components and bundles can be specified on the same command line. When mixing components and bundles on the command line, the filter switches control what components and bundles are installed. |
| /express_install |
This argument starts express install (for local host only). HP SUM performs discovery, install, or exit without user interaction. The user can cancel or terminate HP SUM. |
| /use_location "file_share" |
This argument specifies a directory or file share that contains the PSP, ISP, and components for use with HP SUM. The file_share format must be a mapped file share and not in UNC format. If you do not specify this argument, the directory containing hpsum.exe or HP SUM is used by default. The logged-in account must have access to this location. The /user and /passwd arguments do not have any effect when attempting to access the file share. You can use those arguments only when connecting to a target system. |
| /use_web |
This argument specifies that the checkbox for Check ftp.hp.com on the Source Selection screen is selected. This enables components to be retrieved from hp.com and used in the list of possible updates. This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
| /use_proxy <Proxy server> |
This argument enables the inclusion of a proxy server (and port number) to access ftp.hp.com. This parameter must be used with /use_web. For example, /use_web /use_proxy <1.22.33.44:80>. This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
| /proxy_script <Proxy script> |
This argument enables the inclusion of a proxy script to access ftp.hp.com. This parameter must be used with /use_web. For example, /use_web /proxy_script <autoproxy.com>. This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
| /use_d[ownloaded] |
This argument specifies that the checkbox for Include components previously downloaded from HP.com on the Source Selection screen is selected. This enables those previously downloaded components to be included in the list of possible updates. This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
| /tpmbypass or /ignore_tpm |
This argument specifies that if a TPM is enabled, then the warning message can be ignored and component installation continues. |
| /use_snmp |
This argument specifies that components, which use SNMP protocol, are available to be selected for installation. These components are available for selection by default. When the /use_snmp argument is used, and the /use_wmi argument is not, the WMI components are optional. This argument does not apply to HP Integrity Servers. |
| /use_wmi |
This argument specifies that components, which use WMI protocol, are available to be selected for installation. These components are optional by default and are not installed unless this argument is used. When the /use_wmi argument is used, and the /use_snmp argument is not, the SNMP components are optional. This argument does not apply to HP Integrity Servers. |
| /use_latest |
This argument is a filter switch for use with bundles. The argument enables you to use the latest version of the bundle when multiple versions of bundles are listed on the command line. If no bundles are specified on the command line, and multiple bundles are in the directory, then the /use_latest argument enables HP SUM to use the bundle with the latest version for installation. |
| /romonly |
This argument is a filter switch and enables the user to view only the firmware components required for installation. When using this filter switch, you must exit, and then restart HP SUM to return to an unfiltered state. Do not use the /romonly argument with the /softwareonly argument. (Applies to firmware only.) |
| /softwareonly |
This argument is a filter switch and enables the user to view only the software components required for installation. When using this filter switch, you must exit, and then restart HP SUM to return to an unfiltered state.
Do not use the /softwareonly argument with the /romonly argument. |
| OVERRIDING ERRORS |
| /continue_on_error <error> |
This argument causes the installation to continue and ignore errors. Valid values are:
<error>=ServerNotFound
<error>=BadPassword
<error>=FailedDependencies
The ServerNotFound option can be used to bypass inactive or unavailable remote hosts when deploying firmware or software to multiple remote hosts at the same time. |
| /override_existing_connection |
This argument defines the behavior when a remote target has an existing HP SUM session in progress. This argument overrides the session in progress and reinitializes the installation framework on the remote host. |
| /on_failed_dependency |
This argument informs HP SUM how to proceed when a component has a failed dependency.
The default of OmitHost causes the host to be put in a failure state and no install is attempted on it.
OmitComponent deselects the affected components and proceeds with any updates that do not have dependency failures.
Force attempts all updates, even if they have dependency failures.
|
| REBOOT OPTIONS |
| /r[eboot] |
If the following conditions are met, then this argument causes the server (or host server in a remote installation) to reboot:
- The /reboot option is selected or given as a command-line argument.
- All components selected for installation are successfully installed.
- At least one of the installed components requires a reboot to complete its installation.
|
| /reboot_message "reboot message" |
This argument displays the specified reboot message on remote consoles connected to the server you want to reboot. You must use this argument with the /reboot option or the argument is ignored. |
| /reboot delay timeout_in_seconds |
This argument delays the reboot of the server for the length of time specified by the timeout_in_seconds variable. You must use this argument with the /reboot option, or the argument is ignored. Acceptable values are between 15 and 3600.
- The default timeout value is 15 seconds for Microsoft Windows operating systems and 60 seconds for Linux.
- For Linux, the Reboot Delay time is converted from seconds to minutes, and any value under a full minute, 59 seconds or less, rounds to the next minute.
|
| /reboot_always |
If the following conditions are met, then this argument forces the server to reboot:
- The /reboot_always option is selected or given as a command-line argument.
- All components selected for installation are successfully installed.
|
| CREATING HOST GROUPS |
| /group "group_name" |
This argument specifies an already defined group name in the HP SUM GUI. |
| SIMULATING HP SUM |
| /dryrun |
This argument simulates the installation for a test run. Nothing is installed. |
| TARGETS |
| /user <username> or /username <username> |
This argument enables you to log in to the remote target (except for the OA target) with the user ID. For the OA target, see /oa_username argument. |
| /psswd <password> |
This argument enables you to use the password for the user ID specified in the /user parameter (except for the OA target). The password is used to log in to remote targets. For the OA target, see /oa_password argument. |
| /current_credential |
This argument enables the credentials of the local host to be used as the credentials to access the targets instead of providing the username and password explicitly for each target. The assumption is that the current credentials are valid for the targets being accessed. (Applies to Windows operating systems only.) |
| /target "netAddress" |
This argument is the IP address or the DNS name of a remote server, remote iLO NIC port, Virtual Connect Ethernet or Fibre Channel Module for c-Class BladeSystem, or BladeSystem Onboard Administrator.
When two Onboard Administrators are in an enclosure, this argument should be the active Onboard Administrator. When specifying the IP address, you can use either the IPv4 or IPv6 format. |
| LOG FILES |
| /logdir "path" |
This argument enables you to redirect the output from HP SUM or the HP BladeSystem c-Class Onboard Administrator flash utility to a different directory than the default location.
- For Windows components, the default location is %SYSTEMDRIVE%\CPQSYSTEM\hp\log\<netAddress> and the redirected location is <path>\hp\log\<netAddress>.
- For Linux components, the default location is /var/hp/log/<netAddress> and the redirected location is <path>/hp/log/<netAddress>.
|
| /v[erbose] or /veryv[erbose] |
These arguments enable you to set the verbosity level for the HP SUM execution log file, hpsum_execution_log_<date>_<time>.log. Using one of these arguments increases the level of detail that is retained in the log file. The default value is normal verbosity. |
| GENERATING REPORTS |
| /report |
This argument generates a report listing of the target summary and how the components in the repository affect the target. For example, whether each component applies to the target or not. The report is generated in HTML and XML with the file name formats: HPSUM_Report_<date>_<time>.html and HPSUM_Report_<date>_<time>.xml.
By default, the files are located in the present working directory from where HP SUM is initiated. If that location is write-protected, the report can be found in the same directory as the HP SUM log files.
Including other arguments on the command line can modify the contents of the report. Using the /target argument will allow reports to be generated for different targets. |
| /inventory_report |
This argument generates a report listing of the components in the specified repository. The report is generated in HTML and XML, with file name formats of HPSUM_Inventory_Report_<date>_<time>.html and HPSUM_Inventory_Report_<date>_<time>.xml.
By default, the files are located in the present working directory from where HP SUM is initiated. If that location is write-protected, the report can be found in the same directory as the HP SUM log files.
Including other arguments on the command line can modify the contents of the report. Using the /target argument will allow reports to be generated for different targets. |
| /firmware_report |
This argument generates a report listing of the firmware installed and details of the target. The report is generated in HTML and XML, with file names of HPSUM_Firmware_Report_<date>_<time>.html and fwreport.xml in the directory named HPSUM_Firmware_Report_<date>_<time>.
By default, this directory is located in the present working directory from where HP SUM is initiated. If that location is write-protected, the directory can be found in the same directory as the HP SUM log files.
Including other arguments on the command line can modify the contents of the report. Using the /target argument will allow reports to be generated for different targets.
(This CLI does not apply to firmware updates on the HP Integrity BL860c/BL870c/BL890c i2 Servers.)
|
| USING INPUT FILES |
|
| /inputfile "filename" |
This argument enables you to script the deployment of firmware and software to multiple remote systems at one time. For details of the file format and commands, see the "Input files" section. |
| /deleteinputfile "filename" |
This argument enables you to instruct HP SUM to delete the input file after it has been read in. |
| ENTERING OA CREDENTIALS |
|
| oa_username |
This argument provides the username credential for OA associated with VC specified with "target" command-line parameter. Only one set of OA credentials can be specified with command-line parameters. You can only add multiple VC targets to command-line parameters with "target" parameter if the credentials of OAs associated with specified VCs are the same. The argument oa_username is not required if VC has the same credentials as the associated OA. You do not need to provide an OA network address associated with Virtual Connect. HP SUM queries it from a specified VC target. To update multiple VCs with different username and password or VCs with OAs which have different credentials, the corresponding input files OAUID and OAPWD must be used.
|
| oa_password |
This argument provides the username credential for OA associated with VC specified with "target" command-line parameter. Only one set of OA credentials can be specified with command-line parameters. You can only add multiple VC targets to command-line parameters with "target" parameter if the credentials of OAs associated with specified VCs are the same. The argument oa_password is not required if VC has the same credentials as the associated OA. You do not need to provide an OA network address associated with Virtual Connect. HP SUM queries it from a specified VC target.
To update multiple VCs with different username and password or VCs with OAs which have different credentials, the corresponding input files OAUID and OAPWD must be used. |
Component configuration for Windows components only
To configure components without using the HP Smart Update Manager GUI, issue the command, hpsum_config <component_to_configure>. This command presents the same configuration screens seen in the HP Smart Update Manager GUI. You must run this command from a CD or other read-only media, or the component cannot be configured. Configuration for a given component only needs to be executed one time. The configuration is stored within the component and is propagated to all target servers when deployed through HP Smart Update Manager GUI or command line. To change the configuration, rerun hpsum_config against the component and a new configuration writes out. If a component does not need configuration, the hpsum_config command returns to the console.
To configure components to be deployed on all editions of the Windows Server 2008 with the Server Core option, you must access the system as a remote host using HP Smart Update Manager running on a system with a supported Windows operating system, and then configure the components before deployment.
Command-line examples
The following command-line parameter examples can be executed within these environments:
- Windows PSPs:
- ProLiant Support Pack for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 v7.90 (BP000323.xml)
- ProLiant Support Pack for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 v7.80 (BP000315.xml)
- Firmware:
- System ROM
- Smart Array controller
- Hard drives
- iLO
- Software-later version of:
- HP Insight Diagnostics Online Edition for Windows Server 2003 (cp008097.exe)
- HP Systems Management Homepage for Windows (cp008257.exe)
- HP Smart Update Manager
- Defined groups: Management Servers - Three servers (Management Server1, Management Server2, Management Server3)
Example 1:
This command-line input deploys the latest PSP and firmware components:
hpsum /use_latest /allow_non_bundle_components /silent
Results: All software components from the 7.90 PSP and firmware components, which HP SUM determined are required to be installed, were installed.
Example 2:
Either of the following command-line inputs can deploy the previous version of the PSP only and force all the components to be installed:
Results: All software components from the 7.80 PSP, which HP SUM determined are required to be installed, were installed. No firmware was installed.
Example 3:
This command-line input deploys firmware:
hpsum /romonly
Results: All firmware components, which are required to be installed, were installed. No software was installed.
Example 4:
Either of the following command-line inputs can deploy two software components:
Results: The two components were installed. No firmware or other software was installed.
Example 5:
Either of the following command-line inputs can deploy the latest PSP, later versions of components in the bundle, and firmware to three remote hosts and force all components to be installed:
hpsum /group "Management Servers" /current_credential /use_latest /allow_update_to_bundle /allow_non_bundle_components /force:all /override_existing_connection /continue_on_error ServerNotFound /silent /logdir "Management_Server_Files"
hpsum /target "Management Server1" /target "Management Server2" /target "Management Server3" /user administrator /passwd letmein /use_latest /allow_update_to_bundle /allow_non_bundle_components /force:all /override_existing_connection /continue_on_error ServerNotFound /silent /logdir "Management_Server_Files"
Results: All firmware components, software components from the 7.90 PSP, cp008097.exe, and cp008257.exe were installed on Management Server1, Management Server2, and Management Server3.
Return codes
HP SUM has consolidated return codes from Linux and Windows smart components into a new, enhanced return code mapping. These return codes determine the status of the component installation. You can also use return codes in a script to control the execution of the script and determine any required branching.
In Linux, the negative return codes are reported. These return codes are determined by subtracting the negative value from 256.
To view the installation log file locations, see "Viewing the installation results"
| Return code |
Value |
Linux |
Windows |
Text |
| SUCCESS_NO_REBOOT |
0 |
0 |
0 |
The installation was successful. |
| SUCCESS_REBOOT |
1 |
1 |
1 |
The installation was successful, but a reboot is required. |
| SUCCESS_NOT_REQUIRED |
3 |
3 |
3 |
The component was current or not required. |
| FAILURE_GENERAL |
-1 |
255 |
255 |
A general failure occurred. For details, see the error log. |
| FAILURE_BAD_PARM |
-2 |
254 |
254 |
A bad input parameter was encountered. |
| FAILURE_COMPONENT_FAILED |
-3 |
253 |
253 |
The installation of the component failed. |
Windows smart component return codes
| Error level |
Meaning |
| 0 |
The smart component failed to install. For more details, see the log file. |
| 1 |
The smart component installed successfully. |
| 2 |
The smart component installed successfully, but the system must be restarted. |
| 3 |
The installation was not attempted because the required hardware is not present, the software is current, or there is nothing to install. |
Linux smart component return codes
Single target servers:
| Error level |
Meaning |
| 0 |
The smart component installed successfully. |
| 1 |
The smart component installed successfully, but the system must be restarted. |
| 2 |
The installation was not attempted because the required hardware is not present, the software is current, or there is nothing to install. |
| 3 |
The smart component failed to install. For more details, see the log file. |
Multi-target servers:
| Error level |
Meaning |
| 0 |
The installation of the deliverable is successful. No reboot is required. |
| 1 |
The installation of the deliverable is successful. Reboot is required for the deliverable to be enabled. |
| 2 |
The installation was not attempted because the version to be installed matches the version already installed. |
| 3 |
The installation was not attempted because of one of the following:
- The version to be installed is older than the version already installed.
- The supported hardware is not present, not enabled, or in a state that an installation could not be attempted.
- The smart component does not support the environment.
- There is nothing for the component to accomplish.
|
| 4 |
If the component is installing to a remote target, such as Onboard Administrator or other network-based deployment, this return code indicates that the target cannot be found. |
| 5 |
The installation was canceled by a user before anything could be installed. |
| 6 |
The installer cannot execute because of an unmet dependency or installation tool failure. |
| 7 |
The actual installation operation (not the installation tool) failed. |
Linux RPM return codes
| Error level |
Meaning |
| 0 |
The Linux RPM installation was successful. |
| 1 |
The Linux RPM installation failed. |
Input files
HP SUM provides the ability to script the update of multiple, individual targets or groups of targets (HP ProLiant and Integrity server and options) within a single operation through the input file functionality. To protect your credentials, use a secure server or a management console.
To create an input file, use a text editor. All section headers and trailers [END] must match. Failure to use the SILENT=YES option causes the GUI mode to be used, but the information provided enables you to skip screens where information has already been provided. The DRYRUN=YES option can be used to perform dry runs of installations to ensure the scripts are working without deploying the firmware updates that might be required on each target. Remove the DRYRUN=YES option to perform the updates.
For parameters that can take list values, list separator can be commas, semicolons, or spaces.
|
NOTE: The credentials can be left out of the file for greater security and passed on the command line to HP Smart Update Manager. The only limitation of this is that the userID and credentials must be the same on all.
|
When the file has been created, to use it with HP SUM, add it as the inputfile <filename> parameter to a normal HP SUM command line. For example, if the name of the input file is hpsum.in, the command-line syntax is hpsum -inputfile hpsum.in. Full paths can be added to the input file location if it is not stored in the same location as the HP SUM executables. The <filename> field can be enclosed in double quotes to enable paths with spaces. Also, the input file itself might contain the same flags on the command line. The usual command-line flags can still be used with the -inputfile flag and takes precedence over any given input file.
Command-line usage of input file
The form for the HP SUM command line using an input file is hpsum -inputfile <filename>.
The input file itself can contain the same flags on the command line. The usual command line flags can still be used with the -inputfile flag, and takes precedence over any given input file. The <filename> field can be enclosed in double quotes to enable paths with spaces.
Input file format and rules
The input file is divided into two sections:
- Configuration
The configuration section starts from the beginning of the file and proceeds until the first target section is encountered. This section consists of a number of settings parameters and their values. Each configuration setting must appear on a fresh line in the file along with its value. Comments start with a # character at the beginning of the line. Only one # is allowed on any line.
- Target
You can provide remote host targets to HP Smart Update Manager. This section can repeat any number of times in the input file, providing a way to organize targets in related sets.
The section starts with a special header "TARGETS" enclosed in a pair of square brackets:
[TARGETS]
Targets section ends with the special string "END" enclosed in a pair of brackets:
[END]
The keyword TARGETS can be suffixed with an optional arbitrary string. This enables you to tag the purpose of the TARGETS section. Other than the visible difference in the header, the contents of such a section are not treated any differently. For example,
[TARGETS_WIN2003]
...
[END]
Credentials: The TARGETS section allows the targets to be grouped according to the credentials needed for logging in remotely. Each TARGETS section must have a set of login credentials, which applies to all targets in that section. If you want to use the current host's login credentials to log into one or more remote targets, you can do so by setting the variable USECURRENTCREDENTIAL to YES. Login credentials for one or more hosts can be supplied using the variables UID and PWD. If given at the beginning of a TARGETS section, both variables must be used. If given in the middle of a TARGETS section, one or the other can be used to override the selected variable and continue using the active value for the remaining variable.
Remote Target: A remote target can be specified using the variable HOST. Possible values are a DNS Name or an IP address.
File encoding
To allow for the inclusion of double-byte characters, the input file is in UTF-8 format.
Error reporting
If errors are encountered in the input file, HP Smart Update Manager exits with a return value of -2 (bad parameter). The details of the location and nature of the error are recorded in hpsum_execution_log_<date>_<time>.raw.
Input file parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
Possible values |
| SILENT |
This parameter causes the installation to run silently without GUI or console output. All data is written to the log file. Any generated prompts use the default option and continue the installation without user input. If a component requires input before installation (such as configuration information), then the component installation fails (unless the IGNOREERRORS = "FailedDependencies" parameter is supplied), and an error message is written to the log file. |
YES, NO |
| FORCEALL |
This parameter forces both firmware and software components. |
YES, NO |
| FORCEROM |
This parameter forces updates to firmware components. |
YES, NO |
| FORCESOFTWARE |
This parameter forces updates to software components. |
YES, NO |
| FORCEBUNDLE |
This parameter enables you to override or downgrade an existing installation of components in the selected bundle. |
YES, NO |
| DOWNGRADE |
This parameter enables you to downgrade to an earlier version of firmware for multi-target devices such as hard drives and array controllers. (Applies to firmware only.) |
YES, NO |
| REWRITE |
This parameter enables you to rewrite the same version of firmware only for multi-target devices such as hard drives and array controllers. (Applies to firmware only.) |
YES, NO |
| REBOOTALLOWED |
This parameter enables you to reboot, if required. |
YES, NO |
| REBOOTMESSAGE |
This parameter enables you to create a message to be displayed prior to rebooting. |
Any string (not exceeding 256 characters) |
| REBOOTDELAY |
This parameter enables you to delay before rebooting. |
Time in seconds |
| COMPONENTSLIST |
This parameter enables you to limit the list of components to be updated. |
Component names with file extensions (.exe, .rpm, or .scexe) |
| BUNDLESLIST |
This parameter enables you to limit the list of bundle xml files to be filtered. |
Bundle file names |
| ALLOWUPDATEBUNDLE |
This parameter is a filter switch and enables you to install newer versions of components defined in a PSP, ISP, or bundle.
This parameter enables these components to replace the older versions of the same component that might have shipped with the bundles. |
YES, NO |
| SKIPTARGET |
This parameter defines the behavior when a remote target has an existing HP SUM session in progress.
This parameter enables you to skip the host if an existing HP SUM session already exists. A NO overrides the session in progress and reinitializes the installation framework on the remote host. |
YES, NO |
| IGNOREERRORS |
This parameter causes the installation to continue and ignore errors.
The ServerNotFound option can be used to bypass inactive or unavailable remote hosts when deploying firmware or software to multiple remote hosts at the same time.
FailedDependencies can be used to ignore any failed dependencies and proceed with the ones that are ready to be installed. |
ServerNotFound, BadPassword, FailedDependencies |
| SOURCEPATH |
This parameter can be used to provide a single local repository path. This creates an inventory from the given path instead of the local or default repository. |
Directory path |
| USELATEST |
This parameter is a filter switch for use with bundles. The parameter enables you to use the latest version of the bundle when multiple versions of bundles are listed on the command line.
If no bundles are specified on the command line, and multiple bundles are in the directory, then this parameter enables HP SUM to use the bundle with the latest version for installation. |
YES, NO |
| DRYRUN |
This parameter simulates the installation for a test run. Nothing is installed. |
YES, NO |
| OPTIONS |
This parameter can be used to specify the HP SUM CLI options inside the input file, which overrides the configuration settings. Parameters can be separated by a semi-colon, comma, or a space.
This parameter replaces the LSPOPTIONS parameter that was previously supported with LDU. |
One or more CLI switch |
| USESNMP |
This parameter specifies that components, which use SNMP protocol, are available to be selected for installation.
These components are available for selection by default. When the /usesnmp parameter is used, and the /usewmi parameter is not used, the WMI components are optional. This parameter does not apply to HP Integrity Servers. |
YES, NO |
| USEWMI |
This parameter specifies that components, which use WMI protocol, are available to be selected for installation.
These components are optional by default and are not installed unless this parameter is used. When the /usewmi parameter is used, and the /usesnmp parameter is not used, the SNMP components are optional. |
YES, NO |
| ROMONLY |
This parameter is a filter switch and allows the user to view only the firmware components required for installation.
Do not use the /romonly parameter with the /softwareonly parameter. |
YES, NO |
| SOFTWAREONLY |
This parameter is a filter switch and allows the user to view only the software components required for installation.
Do not use the /softwareonly parameter with the /romonly parameter. |
YES, NO |
| USECURRENTCREDENTIAL |
This parameter enables the credentials of the local host to be used as the credentials to access the targets instead of providing the username and password explicitly for each target.
The assumption is that the current credentials are valid for the targets being accessed. (Applies to Windows operating systems only.) |
YES, NO |
| WEBUPDATENEEDED |
This parameter enables you to instruct HP SUM to include the components from ftp.hp.com in the list of possible updates. (This parameter does not apply to Integrity servers.) |
YES, NO |
| USEPROXYSERVER |
This parameter enables the inclusion of a proxy server (and port number) to access ftp.hp.com. (This parameter does not apply to Integrity servers.) |
String value For example, 11.22.33.44:80 |
| USEPROXYSCRIPT |
This parameter enables the inclusion of a proxy script to access ftp.hp.com. (This parameter does not apply to Integrity servers.) |
Web URL (for example, autoproxy.com) |
| DELETEINPUTFILE |
This parameter enables you to instruct HP SUM to delete the input file after it has been read in. |
YES, NO (default) |
| ONFAILEDDEPENDENCY |
This parameter instructs HP SUM how to proceed when a component has a failed dependency.
The default of OmitHost causes the host to be put in a failure state and no install is attempted on it.
OmitComponent deselects the affected components and proceeds with any updates that do not have dependency failures. Force attempts all updates, even if they have dependency failures. |
OmitHost (default), OmitComponent, Force |
| HOST |
This parameter is the IP address or the DNS name of a remote server, remote iLO NIC port, Virtual Connect Ethernet or Fibre Channel Module for c-Class BladeSystem, or BladeSystem Onboard Administrator.
When two Onboard Administrators are in an enclosure, this parameter is the active Onboard Administrator. When specifying the IP address, you can use either the IPv4 or IPv6 format.
This parameter specifies an already defined group name in the HP SUM GUI. |
IP address, DNS name |
| UID |
This parameter enables you to log in to the target hosts with your user ID. |
<username> |
| PWD |
This parameter enables you to use the password for the user ID specified in the UID.
The password is used to log in to target hosts. |
<password> |
| LOGFILENAME |
This parameter enables you to set the name of the log file generated by HP SUM to something other than the default of /var/log/hppldu.log. The path must already exist or the log file remains the default file name. |
Log file name |
| CMALOCALHOSTRWCOMMSTR |
This parameter enables you to specify an SNMP read/write community string for local host access. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
SNMP read/write community string |
| CMALOCALHOSTROCOMMSTR |
This parameter enables you to specify an SNMP read-only community string for local host access. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
SNMP read-only community string |
| CMAMGMTSTATIONRWIPORDNS |
This parameter enables you to specify the IP address or DNS host name of a system with read/write access to serve as a management station. You can specify multiple locations separated by a space. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
IP address, DNS name |
| CMAMGMTSTATIONRWCOMMSTR |
This parameter enables you to specify an SNMP read/write community string for a system with read/write access that serves as a management station. You can specify multiple strings separated by a space. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
SNMP read/write community string |
| CMAMGMTSTATIONROIPORDNS |
This parameter enables you to specify the IP address or DNS host name of a system with read-only access to serve as a management station. You can specify multiple locations separated by a space. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
IP address, DNS name |
| CMAMGMTSTATIONROCOMMSTR |
This parameter enables you to specify an SNMP read/write community string for a system with read-only access that serves as a management station. You can specify multiple strings separated by a space. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
SNMP read/write community string |
| CMADEFTRAPCOMMSTR |
This parameter enables you to set a default SNMP community string for traps. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
SNMP community string |
| CMATRAPDESTINATIONCOMMSTR |
This parameter enables you to specify the SNMP destination trap community string. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
SNMP trap destination |
| CMATRAPDESTINATIONIPORDNS |
This parameter enables you to specify the IP address or DNS host name of a server as a destination for SNMP traps, such as Systems Insight Manager. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
IP address, DNS name |
| CMASYSCONTACT |
This parameter enables you to specify a person or phone number for administration of this system. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
String value |
| CMASYSLOCATION |
This parameter enables you to designate the location of this system. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
String value |
| CMASTARTWEBAGENT |
This parameter determines whether the HP Insight Systems Manager Web Agent is started when the health application loads. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
- YES (start the web agent)
- NO (do not start the web agent)
|
| CMASTARTSTORAGEAGENT |
This parameter determines whether the HP Insight Systems Manager Storage Agent is started when the health application loads. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
- YES (start the storage agent)
- NO (do not start the storage agent)
|
| CMANOTAINTEDKERNEL |
This parameter determines whether the HP Lights-Out management driver is started when the health application loads. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
- YES (start the HP Lights-Out management driver)
- NO (do not start the HP Lights-Out management driver)
|
| HPVCAVCRMSERVER |
This parameter informs the VCA of the name of the VCRM to use as a software distribution repository. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
VCRM name |
| HPVCAVCRMLOGINID |
This parameter is the login ID that the VCA uses to communicate with the VCRM. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
VCA login ID |
| HPVCAVCRMLOGINPASSWD |
This parameter is the password for the login ID specified in the HPVCAVCRMLOGIN parameter. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
VCA login password |
| ADMIN-GROUP |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage (hpsmh) to set up security for the web server. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
Up to five Linux groups, separated by spaces or semicolons, to enable administrative access to the web services. |
| USER-GROUP |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to set up security for the web server. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
Up to five Linux groups, separated by spaces or semicolons, to enable user-level access to the web servers. |
| OPERATOR-GROUP |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to set up security for the web server. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
Up to five Linux groups, separated by spaces or semicolons, to enable operator-level access to the web servers. |
| ANONYMOUS-ACCESS |
This parameter determines whether an anonymous user can access the HP Systems Management Homepage. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
YES, NO (default) |
| IP-BINDING |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to determine whether hpsmh can use all available NICs and detect subnets for its web services. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
YES, NO (default) |
| IP-BINDING-LIST |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to restrict the NICs and subnets to use for its web servers.
The IP-BINDING parameter must be set to yes for this parameter to be used during installation. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
IP address/NetMask pairs separated by semicolons (for example, 10.1.1.1/255.255.255.0;10.2.2.2/255.255.255.0) |
| IP-RESTRICTED-LOGINS |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to restrict login access. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
YES, NO (default)
To enable restrictions on who can log in to the web server, this parameter must be set to yes, and values must be provided to the IP-RESTRICTED-EXCLUDE or IP-RESTRICTED-INCLUDE parameters. |
| IP-RESTRICTED-EXCLUDE |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to exclude specific IP address/NetMask pairs from logging into the web services. (Applies to Linux PSP only.)
This parameter is ignored unless the IP-RESTRICTED-LOGINS parameter is set to yes. |
List of IP address ranges separated by semicolons (for example, 10.1.1.1-10.1.1.10;10.2.2.2-10.2.2.10) |
| IP-RESTRICTED-INCLUDE |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to enable login only from the IP address/NetMask pairs specified. (Applies to Linux PSP only.)
This parameter is ignored unless the IP-RESTRICTED-LOGINS parameter is set to yes. |
List of IP address ranges separated by semicolons (for example, 10.1.1.1-10.1.1.10;10.2.2.2-10.2.2.10). |
| LOCALACCESS-ENABLED |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to determine whether to enable local anonymous access to the web services. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
- YES (default to include anonymous access)
- NO
|
| LOCALACCESS-TYPE |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to determine the type of access granted to local users. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
- Anonymous (default)
- Administrator
CAUTION: Selecting local access with administrator privileges as the login provides full access to any user with access to the local console, without prompting for a user name or password. |
| TRUSTMODE |
This parameter is used by the HP Systems Management Homepage to set up the trust relationship mode. (Applies to Linux PSP only). |
- TrustByCert - If this value is used, the CERTLIST parameter must be defined to enable access to the server.
- TrustByName - If this value is used, the XENAMELIST parameter must be defined.
- TrustByAll - HP does not recommend using this value because of possible negative security consequences.
NOTE: The accepted values are case-sensitive and must be capitalized as shown. Failure to do so prevents the trust relationship from being set up properly during installation and might affect access to the web server. |
| CERTLIST |
This parameter enables a user to provide a list of certificate files or servers where certificates can be obtained for trust relationships for the HP Systems Management Homepage. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
Certificate file name or Server DNS name |
| XENAMELIST |
This parameter enables a user to provide a list of servers, separated by semicolons, for trust relationships for the HP Systems Management Homepage. (Applies to Linux PSP only.)
This parameter is only valid if the TRUSTMODE parameter is set to TrustByName. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
Server DNS name |
| HPQLA2X00FO |
This parameter is used by the hp_qla2x00 QLogic Fibre Channel Driver to determine the failover mode to use. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
- SinglePath
- SecurePath
- QLogicFailure
(No default value) |
| HPQLA2X00FORCE |
This parameter is used by the hp_qla2x00 QLogic Fibre Channel Driver to determine whether to skip detection of third-party storage. (Applies to Linux PSP only.) |
"Y", "N" (default) |
| OAUID |
This parameter provides the username credentials for OA associated with VC. You must define a value of these variables before HOST variable in [TARGETS] section. This parameter only applies for VC firmware. |
User can define OAUID variable multiple times before each HOST variable. |
| OAPWD |
This parameter provides the password credentials for OA associated with VC. You must define a value of these variables before HOST variable in [TARGETS] section. This parameter only applies for VC firmware. |
User can define OAPWD variable multiple times before each HOST variable. |
Examples of the HP SUM input file include:
REBOOTALLOWED = YES
REBOOTREQUIRED = NO
REBOOTMESSAGE = "Server is going down for a reboot"
REBOOTDELAY = 15
COMPONENTSLIST = cp001234.exe, cp001235.exe
BUNDLESLIST = bp001234.xml
ALLOWUPDATEBUNDLE = YES
SKIPTARGET = NO
IGNOREERRORS = ServerNotFound, FailedDependencies
SOURCEPATH = c:\pkgsource1
USELATEST = YES
SILENT = YES
OPTIONS = /f:rom
[TARGETS]
HOST = schinta1
HOST = schinta2
UID = root
PWD = root123
HOST = 234.567.765.432
[END]
USAGE: hpsum /inputfile <path:\inputfile.txt>
Examples of inputfile.txt file:
Example 1: The two targets are passed to be updated. The targets do not necessarily have to be OAs. They can be any target supported by HP SUM.
DRYRUN = YES
SILENT = YES
[TARGETS]
HOST = BL465C-01
HOST = 192.168.1.2
[END]
Example 2: A host DNS is passed along with the user ID and password to use for the hosts in the group.
DRYRUN = YES
SILENT = YES
[TARGETS]
HOST = BL685cG6
UID = Bigboss2
PWD = password
[END]
Example 3
SILENT = YES
IGNOREERRORS = ServerNotFound,BadPassword, FailedDepedencies
SKIPTARGET = NO
SOURCEPATH = C:\fwcd\firmware-8.70-0\hp\swpackages
[GROUPS]
HOST=winserver
UID=Userid
PWD=password
[END]
Example 4
SILENT = YES
IGNOREERRORS = ServerNotFound,BadPassword, FailedDepedencies
SKIPTARGET = NO
SOURCEPATH = C:\ fwcd\firmware-8.70-0\hp\swpackages
FORCEALL = YES
REBOOTALLOWED = YES
REBOOTDELAY = 30
REBOOTMESSAGE = "Install complete, server will reboot in 30 seconds"
[TARGETS]
HOST=16.83.62.141
UID=Userid
PWD=password
[END]
[TARGETS]
HOST=16.83.61.48
UID=Userid
PWD=password
[END]
[TARGETS]
HOST=16.83.62.196
UID=Userid
PWD=password
[END]
[TARGETS]
HOST=16.83.61.24
UID=Userid
PWD=password
[END]
Reports
HP SUM can generate three types of reports about the specified system or repository. You can only generate the reports using the command-line arguments provided. If no additional arguments are specified on the command line, the local host and default repository locations (the directory where HP SUM was initiated) are used. You can specify a target with appropriate credentials and a repository using other command-line parameters if you want to generate reports for other systems and repositories. For specific commands, see "Command-line interface".
| Report type |
Description |
Report file information* |
| /report |
This argument generates a report listing, a target summary, and how the components in the repository affect the target (for example, whether each component applies to the target or not). Usage: hpsum /report This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
The report files generated are:
- hpsum_Report_<date>.html
- hpsum_Report_<date>.xml
|
| /inventory_report |
This argument generates a report listing of the components in the specified repository. Usage: hpsum /inventory_report. This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
The report files generated are:
- hpsum_Inventory_Report_<date>.html
- hpsum_Inventory_Report_<date>.xml
|
| /firmware_report |
This argument generates a report listing of the firmware in the specified repository. Usage: hpsum /firmware_report. This argument is not supported on HP Integrity Servers. |
The report files generated are hpsum_Report_<date>.html and fwreport.xml is placed in a folder named HPSUM_Firmware_Report_<date> |
The reports are generated as an XML and HTML file which can be viewed in a web browser. The supported browsers for viewing the report files are Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 and Mozilla Firefox 3.5 and above. By default, the reports are located in the current working directory from where HP SUM was initiated. If that current location is write-protected, the reports are located in the same directory as the HP SUM log files.
- On Windows operating systems: C:\cpqsystem\hp\log
- On Linux operating systems: /var/hp/log
When generating the requested report, the HP SUM GUI does not appear. When the report is generated, HP SUM reports the location where the report files can be found.
The following figure illustrates the HP SUM report in HTML format.

The following figure illustrates the HP SUM Inventory report in HTML format.
The following figure illustrates the HP SUM Firmware report in HTML format.

Advanced topics
In this section:
Software component configuration
Server virtualization detection and support
Configuring IPv6 networks with HP Smart Update Manager
Software component configuration
Some components might have required or optional configuration settings. Configuration parameters can include information necessary to set up the component correctly or passwords required for software installed by the component. If the optional configuration data of a component is not provided and the component has not been installed previously, then default values for that configuration data are used. If the component has been previously installed and configured and no changes are made to the configuration data, then the existing configuration information is preserved. Component configuration requires that Smart Components are in a write-accessible location. A CD/DVD or read-only network share is not supported.
Configurable components are indicated in the Optional Actions column on the Select Items to be Installed screen. To configure a component, click Configure Now.
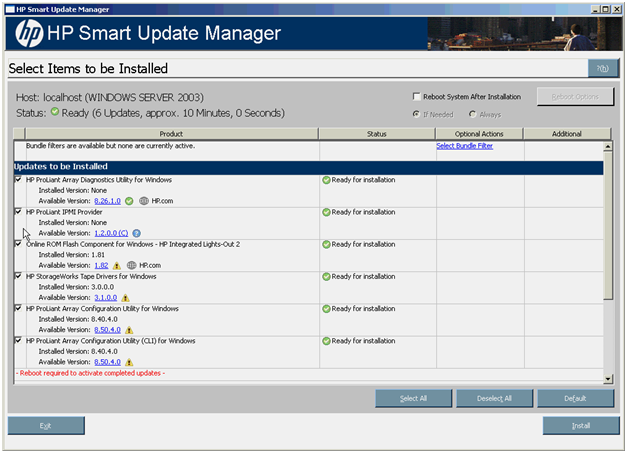
Follow the instructions when the Item Configuration screen appears. When the configuration is complete, the Select Items to be Installed screen reappears.
Deploying firmware and software simultaneously
This topic applies to ProLiant servers and options supported by the server, but does not apply to Integrity servers.
HP SUM utility enables you to deploy firmware and software components simultaneously. The latest firmware and software components must be located in the same directory.
To deploy firmware and software components simultaneously, select the location where the firmware and software components are located in the Source Selections screen. On the Select Bundle Filter screen, select the bundle, and then select the ALLOW NON-BUNDLE PRODUCTS option.
To proceed with the deployment process, click OK. The Select Items to be Installed screen appears with the appropriate firmware and software components.
With the ability to get components from ftp.hp.com (ftp://ftp.hp.com), you can deploy software and firmware components without using bundles.
|
NOTE:Virtual Connect FW components are not available for download from ftp.hp.com using HP SUM at this time.
|
|
NOTE:HP Smart Update Manager is compatible with various types of HP bundles.
|
For more information on the PSPs, see the HP ProLiant Support Pack for Windows and Linux User Guide on the HP website
(http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/DocumentIndex.jsp?contentType=SupportManual&lang=en&cc=us&docIndexId=64179&taskId=101&prodTypeId=18964&prodSeriesId=345557).
Server virtualization detection and support
HP SUM, running in the context of a Windows PSP or ISP, supports server virtualization that runs on a Windows host. However, HP SUM, running in the context of a Windows PSP, does not run on a VMware host or on a guest operating system environment regardless of what host hypervisor you use.
HP SUM, running in the context of the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD, does not support server virtualization that runs on a Windows or Linux host and blocks attempts to install firmware from a guest or child virtual machine. The server virtualization does not run on a VMware host or on a guest operating system environment regardless of which host hypervisor you use. The HP Smart Update Firmware DVD does not boot to a guest operating system environment.
Configuring IPv6 networks with HP Smart Update Manager
Starting with HP Smart Update Manager version 3.2.0, you can deploy to remote targets in IPv6-based networks for Windows and Linux target servers. Using HP Smart Update Manager with IPv6 networks presents challenges for IT administrators.
For Windows-based servers, to communicate with remote target servers, HP Smart Update Manager uses either existing credentials or user-provided user name and password to connect to the admin$ share. This share is an automatic share provided by Windows Server. After HP Smart Update Manager connects to the admin$ share, it copies a small service to the target server for the duration of the installation. After this service starts, HP Smart Update Manager uses this service to communicate between the local and remote target server. During this process, HP Smart Update Manager opens ports in the Windows firewall to enable HP Smart Update Manager to use SOAP calls over SSL to pass data among local and remote systems. These ports are defined in Enabling ports in HP Smart Update Manager. After the installation is completed or canceled, HP Smart Update Manager stops the remote service, removes it from the target server, closes the port on the Windows firewall, and then releases the share to the target server admin$ share.
For Linux-based servers, to communicate to remote target servers, HP Smart Update Manager starts by using the user-provided user name and password to create a SSH connection to the target server. After the HP Smart Update Manager connects, it copies a small service to the target server for the duration of the installation. After this service starts, HP Smart Update Manager uses this service to communicate between the local and remote target server. During this process, HP Smart Update Manager opens ports in the iptables firewall to enable HP Smart Update Manager to use SOAP calls over SSL to pass data between the local and remote systems. These ports are defined in Enabling ports used in HP Smart Update Manager. When the installation is completed or canceled, HP Smart Update Manager stops the remote service, removes it from the target server, closes the port in the iptables firewall, and then closes the SSH connection to the target server.
Configuring IPv6 for Windows Server 2003
For information on setting up a Windows Server 2003 operating system within an IPv6 network, see the online Microsoft Technet article Step-by-Step Guide for Setting Up IPv6 in a Test Lab (http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=fd7e1354-3a3b-43fd-955f-11edd39551d7&displaylang=en).
Before using HP Smart Update Manager to deploy software and firmware updates to remote Windows Server 2003 servers, you must add a registry entry to enable file sharing connections over IPv6 networks. To make the registry entry:
- Start the Registry Editor (Regedt32.exe).
- Locate and click the following key in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- On the Edit menu, click Add Value.
- Add the following registry value:
- Value name: DisableStrictNameChecking
- Data type: REG_DWORD
- Radix: Decimal
- Value: 1
- Quit the Registry Editor.
For more information about these steps, see the Microsoft Knowledge Base Item 281308 on the Microsoft website (http://www.microsoft.com).
IPv6 addresses can be passed to HP Smart Update Manager in command line arguments or using the HP Smart Update Manager user interface. In the HP Smart Update Manager user interface, you can add a remote host on an IPv6 network by either entering the DNS name of the IPv6 target server or by selecting the IPv6 address button and entering the IPv6 address. HP Smart Update Manager supports both the short-name and full IPv6 notation. You do not need to add the optional interface number when you enter the address.

If you cannot connect to the target server or receive a Discovery failed message when executing HP Smart Update Manager in an IPv6 environment, see Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks.
After you connect to the target server, all other HP Smart Update Manager functions work identically. Log files for IPv6 hosts are stored with all other HP Smart Update Manager files in the \CPQSYSTEM\hp\log\<ip_address> directory.
Configuring IPv6 for Windows Server 2008
HP Smart Update Manager provides the most robust support for remote deployment when using Windows Vista as a client to Windows Server 2008-based servers. Using HP Smart Update Manager in this environment enables you to use all the capabilities of IPv6 including link-local, site-local, and global IP addresses for both local and remote target servers. Windows Vista, when used as a client to run HP Smart Update Manager to remote Windows Server 2008 operating systems or as a target operating system on HP Workstation server blades, provides the infrastructure that supports full IPv6 deployment of software and firmware updates from HP Smart Update Manager.
|
NOTE: Windows XP clients are not supported in IPv6 networks for HP Smart Update Manager deployment.
|
IPv6 addresses can be passed to HP Smart Update Manager in command line arguments or using the HP Smart Update Manager user interface. In the HP Smart Update Manager user interface, you can add a remote host on an IPv6 network by either entering the DNS name of the IPv6 target server or by selecting the IPv6 address button and entering the IPv6 address. HP Smart Update Manager supports both the short-name and full IPv6 notation. You do not need to add the optional interface number when you enter the address.

If you cannot connect to the target server or receive a Discovery failed message when executing HP Smart Update Manager in an IPv6 environment, see the Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks.
After you connect to the target server, all other HP Smart Update Manager functions work identically. Log files for IPv6 hosts are stored with all other HP Smart Update Manager files in the \CPQSYSTEM\hp\log\<ip_address> directory.
Limitations of IPv6 for Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2003 requires site-local addresses to provide the necessary file-sharing capabilities needed by HP Smart Update Manager. This means that link-local and global IPv6 addresses are not supported as remote targets with HP Smart Update Manager.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows environments do not have any known limitations to using HP Smart Update Manager.
|
NOTE: Windows XP clients are not supported in IPv6 networks for HP Smart Update Manager deployment.
|
Configuring IPv6 for Linux
HP Smart Update Manager leverages the IPv6 capabilities of Linux as provided by the Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Novell SUSE Linux Enterprise Server products. Using HP Smart Update Manager in this environment enables you to use all the capabilities of IPv6 including link-local, site-local, and global IP addresses for both local and remote target servers. Remote target servers must have the iptables-ipv6 RPM installed before targeting them from HP Smart Update Manager. Failure to install the iptables-ipv6 RPM prevents HP Smart Update Manager from opening the communications port needed to send data to the initiating Linux workstation. You can disable the Linux firewall to allow HP Smart Update Manager to work, but the Linux server becomes vulnerable to attack.
For information on how to setup IPv6 in a Linux environment, see the Linux IPv6 How-To (http://www.linux.org/docs/ldp/howto/Linux+IPv6-HOWTO/index.html).
IPv6 addresses can be passed to HP Smart Update Manager in command line arguments or using the HP Smart Update Manager user interface. In the HP Smart Update Manager user interface, you can add a remote host on an IPv6 network by either entering the DNS name of the IPv6 target server or by selecting the IPv6 address button and entering the IPv6 address. HP Smart Update Manager supports both the short-name and full IPv6 notation. You do not need to add the optional interface number when you enter the address.

If you cannot connect to the target server or receive a Discovery failed message when executing HP Smart Update Manager in an IPv6 environment, see the Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks.
After you connect to the target server, all other HP Smart Update Manager functions work identically. Log files for IPv6 hosts are stored with all other HP Smart Update Manager files in the /var/hp/log/<ip_address> directories.
Limitations of IPv6 for Linux
The only current limitation of HP Smart Update Manager in a Linux IPv6 environment is that all remote target Linux-based servers must have the iptables-ipv6 rpm file installed. You can find the file on the distribution media for both Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Novell SUSE Linux Enterprise Server operating systems. HP Smart Update Manager uses this file to open a port in the IPv6 firewall to communicate with the Linux system that runs HP Smart Update Manager. Failure to install iptables-ipv6 results in HP Smart Update Manager reporting a discovery failure unless you disable the firewall.
Troubleshooting
In this section
Recovering from a failed ROM upgrade
Recovering from an installation failure
Recovering from a discovery failure
Recovering from a loss of Linux remote functionality
Recovering from a blocked program on Microsoft Windows
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks
Enabling ports in HP Smart Update Manager
Recovering from operating system limitations when using a Japanese character set
Recovering from Fatal Error - application will exit message
Recovering from a missing reboot message when running on SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9
Recovering a lost HP Smart Update Manager connection
HP SUM Message 'found new hardware' during discovery process
Non-matching systems error reported when building source Linux RPMs or installing Linux RPMs built from source
Linux component version discrepancy for source RPMs
HP SUM displays No components found in the selected repository(ies) message
Additional/Optional Actions columns are grayed when HP SUM is maximized
Installation of components failed with 'Update returned an error' when installing Linux RPMs
Issues related to bundle filtering on the Select Items to be Installed and Select Bundle Filter screens
HP SUM fails on Vista due to McAfee firewalls
Virtual Connect firmware upgrade using HP SUM fails if VC reports an invalid or bad health state
Recovering from a failed system ROM upgrade
Use redundant ROM or ROMPaq to recover from a system ROM upgrade failure.
Redundant ROM recovery
When you flash the system ROM, ROMPaq writes over the backup ROM and saves the current ROM as a backup, enabling you to switch easily to the alternate ROM version if the new ROM becomes corrupted for any reason. This feature protects the existing ROM version, even if you experience a power failure while flashing the ROM.
When the server boots, the server detects if the current ROM is corrupt. If a corrupt ROM is detected, then the system boots from the backup ROM and sends an alert through POST that the ROM is corrupt.
To access the redundant ROM through RBSU:
- Power up your desktop. A prompt appears in the upper right corner of the screen.
- Access RBSU by pressing F9.
- Select Advanced Options.
- Select ROM Selection.
- Select Switch to Backup ROM.
- Press the Enter key.
- To exit the current menu, press the Esc key, or to exit RBSU, press the F10 key. The server restarts.
If RBSU is inaccessible, then you can switch ROM images by changing the switch settings on the system configuration switch. For more information, see your server documentation.
If both ROM images are corrupt, use ROMPaq recovery.
ROMPaq recovery
The Disaster Recovery feature supports systems that do not support the Redundant ROM feature. Disaster Recovery only applies to platforms with nonredundant system ROM. If both the up-to-date and backup versions of the ROM are corrupt, then perform ROMPaq Disaster Recovery procedures:
- On another server, download and save the ROMPaq image to the hard drive from the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
- Execute the ROMPaq image to create the ROMPaq disk.
- Switch to the server with the corrupted ROM.
- Power down the server.
- Insert the ROMPaq disk.
- Power up the server.
The server generates one long beep and two short beeps to indicate that it is in disaster recovery mode. If the disk is not in the correct drive, then the system continues to beep until a valid ROMPaq disk is inserted.
The ROMPaq disk flashes both system ROM images. If successful, a sequence of ascending audible beeps is generated. If unsuccessful, a sequence of descending audible beeps is generated, and you must repeat the disaster recovery process.
- Power down the server.
- Remove the ROMPaq disk.
- Power up the server.
To manually set the server for ROMPaq disaster recovery:
- Power down the server.
- Remove the access panel.
- Set the system maintenance switch positions for disaster recovery. Switch positions are server-specific. For information about the correct settings for your server, see the server documentation.
- Insert a ROMPaq diskette with the latest system ROM from the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support).
- Install the access panel.
- Power up the server.
- Allow the system to boot completely.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2.
- Reset the system maintenance switch positions to the original settings.
- Repeat steps 5 and 6.
Recovering from a failed option ROM upgrade
To recover from an option ROM upgrade failure, use the recovery method that is appropriate to the specific option.
Array controller ROMs
Array controllers support Recovery ROM, which is a redundancy feature that ensures continuous system availability by providing a backup ROM. During the flash process, a new version of the firmware can be flashed to the ROM while the controller maintains the last known version of the firmware. If the firmware becomes corrupt, the controller reverts back to the redundant version of the firmware and continues operating.
|
NOTE: Storage option ROMs cannot be downgraded with ROMPaq because ROMPaqs have been retired as a delivery method for storage options.
|
Lights-Out management ROMs
To perform disaster recovery for RILOE II, iLO, and iLO 2, see the documentation for your particular Lights-Out management product on the Remote management website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out).
Recovering from an installation failure
Collecting trace directories
HP Smart Update Manager generates a set of debug trace logs located in the %TEMP%\hp_sum directory on Windows systems and \tmp\hp_sum on Linux systems. These files contain internal process and debug information, which can be useful in determining HP Smart Update Manager failures.
|
NOTE: To break out to a Linux console while booted to the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD, press Ctrl Alt d b x. Each key (d, b, x) is hit in succession. This command allows you to collect logs from the \tmp\hp_sum directory. |
Examine the OpMan.trace, IPScout.trace, OSScout.trace, InstallClient.log, and InstallManager.log trace files to determine the cause of the failure. These files provide the following information.
| Trace files |
Function |
| OpMan.trace |
Provides operations trace of the overall installation process. |
| IPScout.trace |
Provides the information on whether the remote target might be contacted and the type of target found (iLO, server, VC, OA). |
| OSScout.trace |
Provides the details of the connection setup and is responsible for cleaning up after an installation and initiating a reboot, if needed and selected by the user, on the target system. |
| InstallClient.log |
Provides the details of the execution of the individual components, including the command line parameters, used to launch the components and the component return code before it is converted to HP Smart Update Manager return codes. |
| InstallManager.log |
Provides the interaction between the Operations Manager and the remote installation client. Any failure in network communications is reported in this file and surfaced as an Installation Failed message for the affected component and potentially all components that follow the failing component. |
| discagent.trace |
Provides the details of the execution of the discovery agent on either the local system during a local installation or the remote target server. If a discovery tool fails, it is reported to this trace file and surfaced as a Discovery Failed message. |
| discmanager.trace |
Provides the interaction between the Operations Manager and the remote discovery client. If a discovery tool fails, it is reported to this trace file and surfaced as a Discovery Failed message. |
It is possible to look in the OpMan.trace file and see which component was winnowed from the installation set and which ones were added. Normally, components are winnowed if:
They do not support installation on the given OS
The hardware they are designed for is not discovered to be present in the server
The component is not for the type of target selected
The component does not report itself capable of being deployed to a given target
The component cannot be deployed in either the online or offline environment HP Smart Update Manager detects it is running in
The component is for a particular class (p-Class or c-Class) of BladeSystem enclosure and the component does not find that class of enclosure.
The following is an example of the output trace in the OpMan.trace on how to determine if a component was prevented from being shown on the Select Items to Install screen or being deployed from the silent console mode. In the example, the binary image files 0.bin and 1.bin (which represented iLO firmware files), components cp011301.exe and cp011500.exe, and the HP BladeSystem Firmware Update Bundle for Windows represented by bundle file bp000648.xml were added to the installation set. All the other components were removed for various reasons.
InstallSet.cpp[212]: Winnow--Adding FileName 0.bin
InstallSet.cpp[212]: Winnow--Adding FileName 1.bin
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName 2.bin
InstallSet.cpp[212]: Winnow--Adding FileName cp011301.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011321.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011489.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011497.exe
InstallSet.cpp[212]: Winnow--Adding FileName cp011500.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011504.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011505.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011550.exe
InstallSet.cpp[222]: Winnow--Removing FileName cp011560.exe
InstallSet.cpp[242]: Target 0: Added Bundle bp000648.xml
Recovering from a discovery failure
Troubleshooting connection errors
If you are receiving an HP SUM Connection Error or Discovery Failed messages, follow these troubleshooting tips:
- Ensure your workstation does not have an existing connection to the ADMIN$ share on the target IP address. If it does, it prevents HP SUM from connecting to the remote server's share because Windows only allows one connection from a client to a server's share. This can be verified by entering net use at a command prompt. If a share to the target IP address \admin$ share exists, delete it, and then attempt the installation again.
- Ensure that the target IP address server's admin$ share is accessible. Validate the target server can be accessed by entering net use x: \\<ip_address_or_dns_name>\admin$ for the target server IP address or DNS name. When the connection is validated, ensure that it is deleted by entering net use x: /d at the command prompt.
- Ensure the user ID being used to connect to the target IP address server is part of the administrator's group. If it is not, HP SUM blocks installation to the target.
- Ensure WMI is enabled and running on all Windows target servers.
- For Windows target servers, enter the username in DOMAIN\USER format, where <user> is the administrative username, and <domain> is either the NETBIOS computer name or the AD domain name for this user account.
- For Linux, ensure the SSH port is not blocked.
- In rare cases, external storage enclosures might cause HP SUM to report a discovery failure or to hang. To resolve this issue, disconnect the external storage until the firmware updates are completed.
- For Linux, ensure that the target server can be contacted through SSH and that the scp command is available to securely send files to the target server.
- Ensure the firewall ports on any routers in the network as documented in the Enabling ports in HP Smart Update Manager section of this document.
- The Symantec End Point Protection product (SEP) blocks HP SUM ability to communicate with remote targets if the Network Threat Analysis feature is enabled. Disable this feature while HP SUM is in use on the workstation.
- Examine the OpMan.trace, IPScout.trace, OSScout.trace, discagent.trace, and discmanager.trace files to determine the cause of the failure. For more information, see Collecting trace directories.
- Ensure the server has a valid serial number.
HP SUM hangs during discovery
If a system hang is observed during HP SUM discovery and the system is connected to external storage, in most cases disconnecting the external storage should resolve the issue.
Recovering from a loss of Linux remote functionality
Configuring firewall settings
When the Unable to Access Host message appears, the target firewall is enabled. By default, the target firewall is enabled in Linux.
To recover remote Linux functionality, the target and host firewall must be disabled or reconfigured to allow IP traffic through the ports needed by HP Smart Update Manager to deploy firmware. For a list of the ports that need to be configured in the firewall, see Enabling ports in HP Smart Update Manager.
Recovering from a blocked program on Microsoft Windows
Configuring Windows firewall settings
The Windows Security Alert appears when a program is blocked from accepting connections from the Internet or a network.

To set the rules for the Windows Firewall and Security Policy, click Unblock, and then set your firewall settings to the following:
- Click Start>Control Panel>Administrative Tools>Windows Firewall with Advanced Security>Inbound Rules>Remote Administration (NP-IN).
- Select Enabled, and then select Allow the connections.
For Direct to iLO support, you must enable ping.
Enabling ports in HP Smart Update Manager
The ports that HP Smart Update Manager uses cannot be configured. When HP Smart Update Manager port initiates communications to remote targets, it uses several well-known ports depending on the operating system. For Windows, it uses ports 138 and 445 to connect to remote targets (equivalent to remote and file print share functionality). For Linux, HP Smart Update Manager uses port 22 (SSH) to start the communications with the remote target.
HP Smart Update Manager uses defined ports to communicate between the remote target and the workstation where HP Smart Update Manager is executing. When you run HP Smart Update Manager, it uses the administrator/root privileges to dynamically register the port with the default Windows and Linux firewalls for the length of the application execution, then closes and deregisters the port. All communications are over a SOAP server using SSL with additional functionality to prevent man-in-the-middle, packet spoofing, packet replay, and other attacks. The randomness of the port helps prevent port scanning software from denying service to the application. The SOAP server is deployed on the remote target using the initial ports described above (ports 138, 445, and 22) and then allocates another independent port as documented below for its communications back to the workstation where HP Smart Update Manager is running. During shutdown of HP Smart Update Manager, the SOAP server is shutdown and removed from the target server, leaving the log files.
To deploy software to remote targets on their secure networks using HP Smart Update Manager, the following ports are used.
For Windows
| Ports |
Description |
Ports 445 and 137/138/139
(Port 137 is used only if you are using NetBIOS naming service.) |
These ports are needed to connect to the remote ADMIN$ share on target servers. These are the standard ports Windows servers use to connect to remote file shares. If you can connect remotely to a remote Windows file share on the target server, then you have the right ports open. |
| Ports 60000-60007 |
Random ports are used in this range to pass messages back and forth between the local and remote systems via SSL. These ports are used on the system running HP Smart Update Manager to send data to the target server.
Several internal processes within HP Smart Update Manager automatically use the port from 60000 when no other application uses it. If there is a port conflict, the manager uses the next available one. There is no guarantee that the upper limit is 60007 as it is dependent on how many target devices are selected for installation. |
| Ports 61000-61007 |
These ports are used from the target server back to the system running HP Smart Update Manager. The same mechanism is used by the remote access code as the 60000 ports, with the first trial port as 61000. There is no guarantee that the upper limit is 61007 when a conflict occurs. For the case of ipv4-only and one NIC, the lowest available one is used by HP Smart Update Manager to pass information between processes on the local workstation where HP Smart Update Manager is executed, and the next available one is used to receive messages from remote servers. |
| Port 62286 |
This port is the default for some internal communications. It is the listening on the remote side if there is no conflict. If a conflict occurs, the next available one is used. |
| Ports 80 or 63000-63005 |
The logs are passed to the target and the logs are retrieved via an internal secure web server that uses port 80 if it is available or a random port between 63000 and 63005, if it is not. This support allows updates of the iLO firmware without the need to access the host server and allows servers running VMware or other virtualization platforms to update their iLO without the need to reboot their server or migrate their virtual machines to other servers. |
For Linux
| Ports |
Description |
| Port 22 |
This port is establishes a connection to the remote Linux server via SSH. |
| Ports 60000-60007 |
Random ports are used in this range to pass messages back and forth between the local and remote systems via SSL. These ports are used on the system running HP Smart Update Manager to send data to the target server.
Several internal processes within HP Smart Update Manager automatically use the port from 60000 when no other application uses it. If there is a port conflict, the manager uses the next available one. There is no guarantee that the upper limit is 60007 as it is dependent on how many target devices are selected for installation. |
| Ports 61000-61007 |
These ports are used from the target server back to the system running HP Smart Update Manager. The same mechanism is used by the remote access code as the 60000 ports, with the first trial port as 61000. There is no guarantee that the upper limit is 61007 when a conflict occurs. For the case of ipv4-only and one NIC, the lowest available one is used by HP Smart Update Manager to pass information between processes on the local workstation where HP Smart Update Manager is executed, and the next available one is used to receive messages from remote servers. |
| Port 62286 |
This port is the default for some internal communications. It is used for listening on the remote side if there is no conflict. If a conflict occurs, the next available one is used. |
| Ports 80 or 63000-63005 |
The logs are passed to the target and the logs are retrieved via an internal secure web server that uses port 80 if it is available or a random port between 63000 and 63005, if it is not. This support allows updates of the iLO firmware without the need to access the host server and allows servers running VMware or other virtualization platforms to update their iLO without the need to reboot their server or migrate their virtual machines to other servers. |
Recovering from operating system limitations when using a Japanese character set
Displaying the user-specified reboot message using a Japanese character set when running on a Linux operating system
You might specify a message to appear before the system shuts down during a reboot operation. When using a Japanese character set and running on a Japanese version of a Linux operating system, the message does not appear properly.
Rebooting with the user-specified reboot message using a Japanese character set when running on a Windows operating system
You might specify a message to appear before the system shuts down during a reboot operation. When using a Japanese character set and running on a Japanese version of a Windows operating system, the message causes the reboot not to occur automatically.
For a successful reboot, you must click Exit. When the message is entered using CLI, the reboot message looks corrupted since the Japanese character set is not supported in CLI.
Recovering from Fatal Error - application will exit message
Running in a directory path containing double-byte characters
When running in a directory path containing double-byte characters, HP SUM hangs while trying to initialize.
The HP Smart Update Manager cannot be run in directories containing double-byte characters in the path name. Paths can be created with double-byte characters when using certain versions of the operating system, such as Japanese or Chinese.
Recovering from a missing reboot message when running on SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9
Running HP Smart Update Manager on SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9
You can specify a reboot message that appears before a server reboots after a successful installation of firmware or software. However, when running HP SUM on SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9, the reboot message does not appear because there is no access to the console when using SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9. This error is not unique to HP SUM, and it is an operating system limitation.
|
NOTE: HP SUM is no longer supported on SUSE Enterprise Linux 9.
|
Recovering a lost HP Smart Update Manager connection
HP Smart Update Firmware DVD mounted using iLO virtual media
When either iLO and NIC firmware are updated, the HP SUM connection is lost and cannot install components.
Booting the Firmware DVD from iLO virtual media is only supported in Offline Automatic Firmware Update mode. Users attempting to boot in this manner might experience issues from connection timeouts, difficulties updating iLO firmware, and mouse syncing issues. If an access error exists, HP SUM cancels the installation.
Component installation fails on a remote target after iLO firmware is installed using HP Smart Update Manager.
When using HP SUM to install software and/or firmware components to a remote target and the iLO firmware is selected for installation, all components to be installed after the iLO firmware is installed will fail with the message: Unable to run component due to access error.
This occurs because the iLO connection between the system running HP SUM and the remote target gets reset when the iLO firmware is updated. The issue will not be seen if the iLO firmware component is not selected for installation.
To resolve this issue:
- Update the iLO firmware by selecting the iLO as a target. Then, update the other software and/or firmware components on the remote target.
- Update the iLO firmware on the remote target first and then update the other software and/or firmware components on the remote target.
|
NOTE: iLO refers to iLO, iLO2, and iLO3.
|
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 networks
If HP Smart Update Manager cannot connect to the remote server, you might receive a Discovery Failed error. Discovery failures can be caused by third-party storage, failure to access the remote target server, and an inability to access system resources. For IPv6 networks, host discovery failures can be caused by the incorrect configuration of the IPv6 network.
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Windows Server 2003 environment
To validate that the IPv6 network is configured correctly for HP Smart Update Manager support, you must verify the following based on your operating system version.
- Validate that the addresses are site-local. Site-local addresses normally start with "FEC0:". Global and link-local IPv6 addresses are not supported when the remote target is Windows Server 2003.
- Validate that you can ping the remote target server. With Windows operating systems, you can still use the ping command to ping IPv6 addresses: ping <ipv6 address>.
- Ensure you can ping the IPv6 loopback address: ping ::1.
- Use the DNS hostname instead of IPv6 address to ensure the address is correct.
- Ensure you have installed the IPv6 protocol. It is not installed by default in Windows Server 2003. Be sure to reboot the server after installing the protocol to ensure addresses are properly obtained.
- Verify that you can connect to the admin$ share using the credentials within HP Smart Update Manager by issuing the following command at a console prompt:
net use * \\<ipv6-address>.ipv6-literal.net\admin$ /user:<username>
net use * \\fec0::2.ipv6-literal.net\admin$ /user:administrator
You might need to provide the password if you are using a user name that is not the same as you used to log in to the local system. All network shares require the use of the .ipv6-literal.net name string to be properly configured by Windows.
|
NOTE: You do not need to use the .ipv6-literal.net suffix when entering IPv6 address into the HP Smart Update Manager user interface or when passing IPv6 address using command line parameters to HP Smart Update Manager.
|
After you validate that you can access the admin$ share on the remote target server, HP Smart Update Manager works unless other network or hardware issues exist.
- Ensure you have made the registry change on remote target servers as mentioned in the HP Smart Update Manager Usage in a Windows Server 2003 IPv6 environment.
- Move back to an IPv4 network address to ensure HP Smart Update Manager properly finds the remote target server without any issues.
You can always copy HP Smart Update Manager to the target servers and execute using the local installation method.
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Windows Server 2008 environment
To validate that the IPv6 network is configured correctly for HP Smart Update Manager support, you must verify the following based on your operating system version.
- Validate that you can ping the remote target server. With Windows operating systems, you can use the ping command to ping IPv6 addresses: ping <ipv6 address>.
- Ensure you can ping the IPv6 loopback address: ping ::1.
- Use the DNS hostname instead of IPv6 address to ensure the address is correct.
- Verify that you can connect to the admin$ share using the credentials within HP Smart Update Manager by issuing the following command at a console prompt:
net use * \\<ipv6-address>.ipv6-literal.net\admin$ /user:<username>
net use * \\fec0::2.ipv6-literal.net\admin$ /user:administrator
You might need to provide the password if you use a user name that is different from the one you used to log in to the local system. All network shares require the use of the .ipv6-literal.net name string to be properly configured by Windows.
After you validate you can access the admin$ share on the remote target server, HP Smart Update Manager works unless there are other network or hardware issues.
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Red Hat and Novell SUSE-based Linux environments
HP SUM found new hardware message
During the discovery progress, HP SUM might display the following pop-up message: Found New Hardware. This message appears because one of the self-discovery components is loading a new driver and the Windows operating systems discovers it as a new piece of hardware.
Similar pop-up messages might occur with Windows 2008 operating systems when the Allow Non-bundle version option on the Select Bundle Filter screen is selected.
Non-matching systems error reported when building source Linux RPMs or installing Linux RPMs built from source
If HP SUM reports non-matching systems error when trying to build source Linux RPMs or installing Linux RPMs built from source, then the operating system on the target server does not match the operating system from which you are running HP SUM in one of the following ways:
- The distribution of the operating system does not match. For example, RHEL 4.7 and RHEL 4.8 would be a mismatch.
- The architecture of the two operating systems does not match. For example, one server might be running an operating system with x86 architecture and the other with x86_64 architecture.
- The kernel version running on the two systems does not match.
Resolution options:
- Run HP SUM on the target server itself instead of remotely deploying HP SUM.
- Build the driver RPM locally and take the resulting RPM file from the standard location (for example, /usr/src/redhat/RPMS/i686/<driver>.rpm) and then copy it back into the HP SUM repository. HP SUM will pick up the pre-built RPM and enable the user to deploy it anywhere they choose.
Linux component version discrepancy for source RPMs
You might observe differences in the RPM component name which might appear to be a version mismatch for the component on the Select Item to be Installed screen and the Installation Results screen. This is caused by the RPM build phase. The resulting component is actually the same version. The RPM build adds information, so it is technically the same component.
For example, if you select the component HP NC Series Mellanox 10GBE Driver for Linux on the Select Items to be Installed screen, it appears as hp-minx-en-1.4.3.1-1.src.rpm and on the Installation Results screen, it appears as hp-minx-en-kmp-default-1.4.3.1_2.6.27.19_5-1.x86_64.rpm.
HP SUM displays No components found in the selected repository(ies) message
The No components found in the selected repository(ies)error appears when at least one space is in the path name of the repository containing the components to be installed.
To resolve this issue, make sure no spaces are in the path name.
Additional/Optional Actions columns are grayed when HP SUM is maximized
If the Select Items to be Installed screen or Installation Results screen in HP SUM is maximized, the Additional column and sometimes the Optional Actions columns are grayed out.
To resolve this issue, restore the screen to the original size.
Installation of components failed with 'Update returned an error' when installing Linux RPMs
When installing any component, if the installation fails, then HP SUM displays Update returned an error message. To determine the installation failure, review the associated component log.
However, when installing RPMs using HP SUM you might see this error when the RPMs for more than one Linux distribution are present in a single repository and a PSP bundle from the Select Bundle Filter screen is not selected.
In this scenario, when multiple versions of source RPMs exist, the RPMs that are not the latest are not installed and Update not needed or Not Updated-already current messages are returned. HP SUM cannot determine which source RPMs go with which distribution because the RPMs do not contain any operating system information.
To resolve this issue, make sure to select the bundle for the OS distribution on the Select Bundle Filter screen for installation or remove the RPMs from the directory that are not applicable to the Linux distribution you are using.
Issues related to bundle filtering on the Select Items to be Installed and Select Bundle Filter screens
If you specify a bundle to use for installation when starting HP SUM (for example, hpsum /b bp000690.xml), you might experience one or more of the following:
- No bundles listed on the Select Bundle Filter screen.
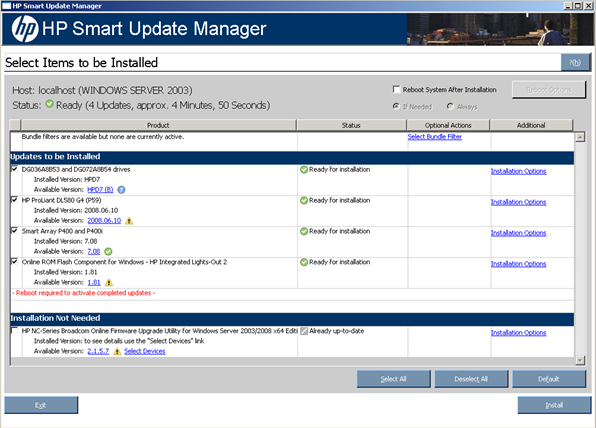
If you specify a bundle when starting HP SUM, then the Select Bundle Filter screen is not shown and the Select Items to be Installed screen appears with the specified bundle listed as the filter. This is expected, as a bundle was preselected.
If you then select the Select Bundle Filter link, then the Select Bundle Filter screen appears with no bundles available for selection. This issue occurs because HP SUM only recognizes the specified bundle and no others, even if other bundles are present in the repository. Even though this issue occurs, HP SUM is working as designed.
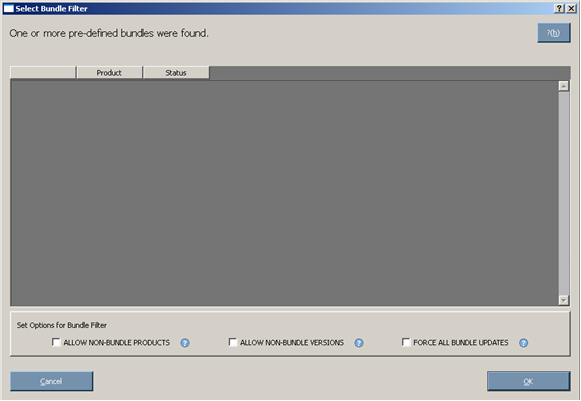
- No bundle being used as a filter on the Select Items to be Installed screen.
If you experience the first issue and then select OK on the Select Bundle Filter screen to return to the Select Items to be Installed screen, the bundle you originally specified is no longer listed as the filter. To use your bundle as the filter, you must exit and restart HP SUM.

If this issue occurs, from the GUI run HP SUM.
HP SUM fails on Vista due to McAfee firewalls
This is a known issue with McAfee that McAfee firewalls block HP SUM traffic.
To resolve this issue, enable the port traffic associated with the HP SUM application by performing the following steps:
- From the system tray, click the McAfee icon.
- Select Manage Features.
- Select McAfee Host Intrusion Protection.
As displayed in the following image, in the Message column, notice the entry similar to the following: Blocked Incoming TCP from the HOST (15.255.101.110) during execution of HP SUM.
- From the menu, select Task>Unlock Interface.
- Copy and then paste the following password: WObeQZGDCAG4
|
NOTE: This password expires on April 7, 2011. |
- Select the Firewall Policy tab.
- On the bottom of the screen, click Add.
- From the screen image, use the following settings for the new firewall rules on your system.

- Click OK to ensure new firewall rules have been implemented.
- Restart HP SUM. Performing this step does not allow HP SUM to function, although after a period of time (ranging from minutes to hours), McAfee disables HP SUM access.
Virtual Connect firmware upgrade using HP SUM fails if VC reports an invalid or bad health state
Virtual Connect firmware can be upgraded using HP SUM only if the health state of the VC is in a good state. If the health state is invalid or bad, HP SUM does not upgrade the VC firmware.
If a VC upgrade is attempted in an invalid or bad health state, HP SUM installation fails. The details of the failure can be viewed in the installation log by clicking the View Installation log link in the Additional section.
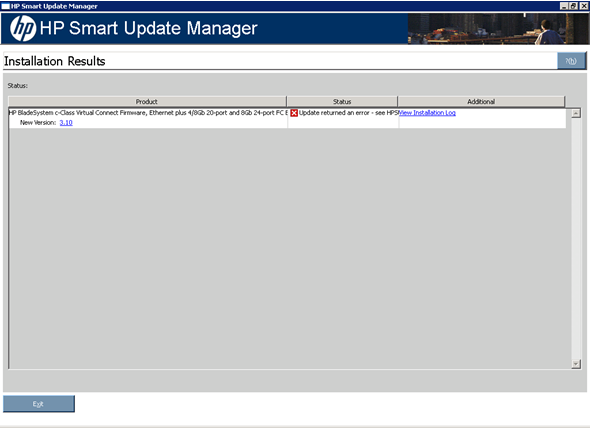
Some of the VCSU Health Status bad states are:
- VC module is not redundant
- Cannot authenticate to OA (bad OA IP or User/Pass) or to VCM (bad VCM IP or User/Pass)
- Could not retrieve a list of modules in the domain or the module is empty
- For any modules, the power is not ON, the hardware health is not OK, cannot connect to module IP address, or the module role is Unknown
- OA version is version 3.00 or earlier, or the VLAN feature is enabled and VC modules are on a different VLAN ID than OA
- VCM Domain checkpoint is not valid
- VCM Module adjacent to the Primary VCM is not compatible with the Primary VCM
To resolve this issue, the VCSU must be used to upgrade the firmware.
Technical support
In this section
Reference documentation
Operating system information
HP contact information
Reference documentation
- To download the ProLiant Firmware Maintenance CD, Smart Update Firmware DVD, SmartStart, and other CD/DVDs, see the SmartStart download website (http://www.hp.com/go/ssdownloads).
- For information about firmware support, see the ProLiant Firmware Maintenance CD/DVD Matrix (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart/supportmatrices).
- For information about SmartStart support, see the SmartStart support matrices (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart/supportmatrices).
- To download the latest PSPs, see the software and drivers download page (http://www.hp.com/servers/swdrivers).
- For more information about PSPs, see the PSP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/psp).
- For more information about ISPs and Windows on Integrity releases, see the Integrity website (http://h20341.www2.hp.com/integrity/w1/en/os/windows-on-integrity-releases.html).
- For more information about Windows on Integrity support, see the support matrices (http://h20341.www2.hp.com/integrity/w1/en/os/windows-on-integrity-support-matrix.html).
- To download the Integrity Smart Setup, Management, or Smart Update DVDs, see the Integrity website (http://h20341.www2.hp.com/integrity/w1/en/software/essentials-windows-on-integrity.html).
- For an overview of the HP Integrity family of servers, see the Integrity website (http://www.hp.com/go/integrity).
- For information on Integrity firmware update options, see the HP website (http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/Document.jsp?lang=en&cc=us&objectID=c00399523&jumpid=reg_R1002_USEN).
- For other documents supporting the Windows Server operating system on HP Integrity servers, see the Windows on Integrity documents (http://www.hp.com/go/windows-on-integrity-docs).
- For information about HP Subscriber's Choice, see the Subscriber's Choice website (http://www.hp.com/go/subscriberschoice).
- For information about the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit, see the Toolkit website (http://www.hp.com/servers/sstoolkit).
- For information about the HP Insight Control server deployment software, see the HP Insight Rapid Deployment software website (http://www.hp.com/servers/rdp).
- For information about operating systems supported by ProLiant servers, see the operating system support matrices (http://www.hp.com/go/supportos).
Operating system information
For information about Microsoft Windows operating systems, see the Microsoft website (http://www.microsoft.com).
For information about Linux operating systems, see one of the following websites:
- Red Hat Linux (http://www.redhat.com)
- SUSE Linux (http://www.novell.com/linux)
HP contact information
For the name of the nearest HP authorized reseller:
- See the Contact HP worldwide (in English) webpage (http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/wwcontact.html).
For HP technical support:
- In the United States, for contact options see the Contact HP United States webpage (http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/contact_us.html). To contact HP by phone:
- Call 1-800-HP-INVENT (1-800-474-6836). This service is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
- If you have purchased a Care Pack (service upgrade), call 1-800-633-3600. For more information about Care Packs, see the HP website (http://www.hp.com/hps).
- In other locations, see the Contact HP worldwide (in English) webpage (http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/wwcontact.html).
Acronyms and abbreviations
BMC
Baseboard Management Controller
CLI
Command Line Interface
CPLD
complex programmable logic device
FPGA
Field Programmable Gate Array
GUI
graphical user interface
HBA
host bus adapter
HP SUM
HP Smart Update Manager
I/O
input/output
iLO
Integrated Lights-Out
iLO 2
Integrated Lights-Out 2
iLO 3
Integrated Lights-Out 3
ISP
Integrity Support Pack
LDU
Linux Deployment Utility
NIC
network interface controller
OA
Onboard Administrator
POST
Power-On Self Test
PSP
HP ProLiant Support Pack
RBSU
ROM-Based Setup Utility
RDP
Rapid Deployment Pack
RILOE II
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition II
SAN
storage area network
SAS
serial attached SCSI
SCSI
small computer system interface
SEP
Symantec Endpoint Protection
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
SOAP
Simple Object Access Protocol
SPLD
System Programmable Logic Device
SSH
Secure Shell
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer
TPM
trusted platform module
VC
Virtual Connect
VCA
Version Control Agent
VCRM
Version Control Repository Manager
VCSU
Virtual Connect Support Utility
WMI
Windows Management Instrumentation
























































